Pyramids of Wonder
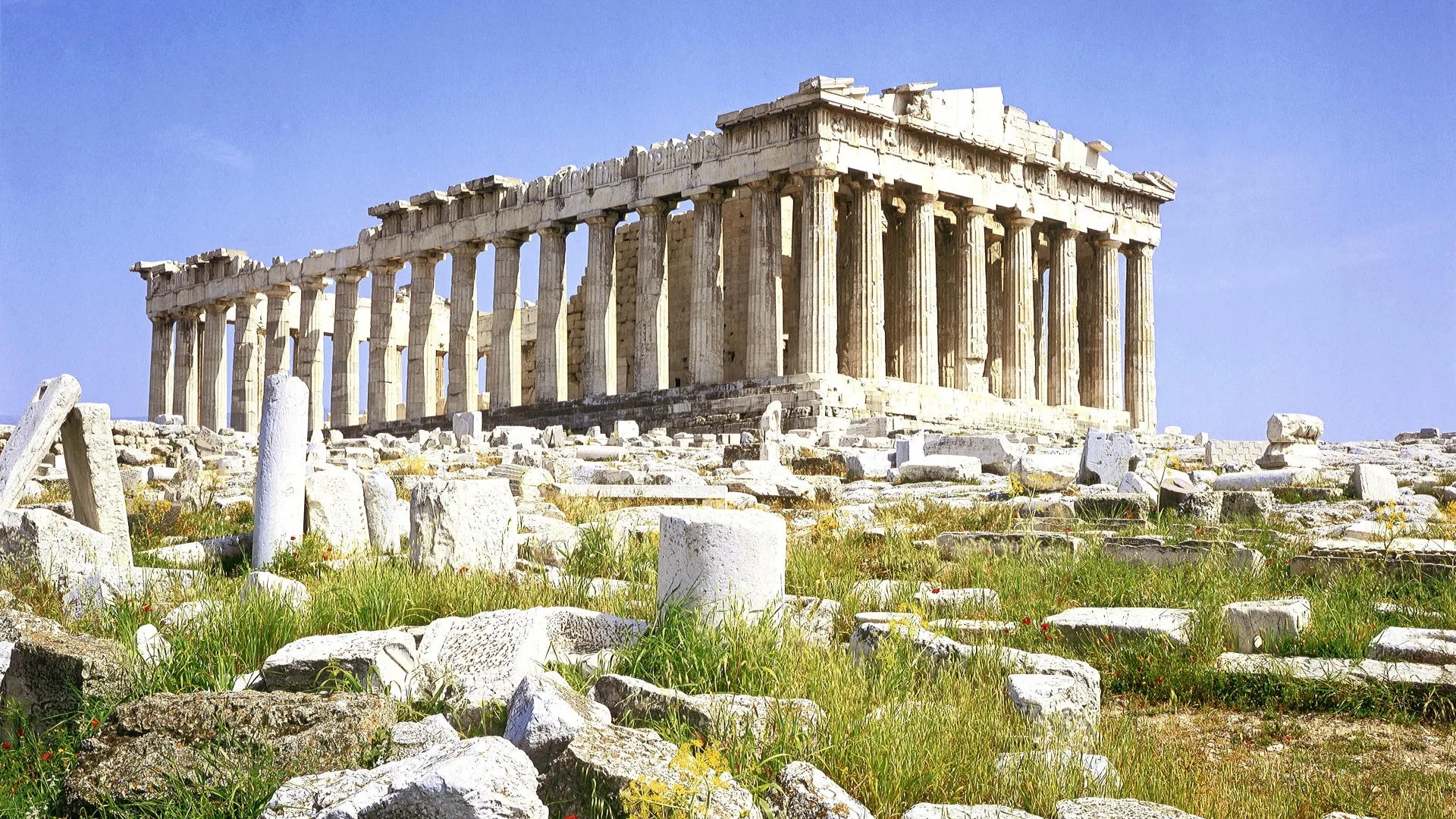
The Great Pyramids of Giza
The Pyramids of Wonder, specifically the Great Pyramids of Giza, are one of the most fascinating and awe-inspiring ancient monuments in the world.
Located on the outskirts of modern-day Cairo, these pyramids have been a source of fascination for centuries, with many questions still surrounding their construction and purpose.
Here are six interesting facts about the Great Pyramids of Giza:
The largest pyramid, known as the Pyramid of Khufu, is an absolute marvel of engineering. It stands at an impressive 481 feet (147 meters) tall and was originally around 491 feet (150 meters) tall when it was first built.
It’s estimated that over 2 million blocks of stone were used to build the Pyramid of Khufu, each weighing an average of 2.5 tons! The pyramid is made up of around 10 million individual stones.
The pyramids were built as tombs for the pharaohs who ruled ancient Egypt. Inside the Pyramid of Khufu, you can see a narrow passageway that leads to a series of chambers and tunnels.
One of the most impressive features of the Great Pyramids is their sheer scale. The Pyramid of Khufu is surrounded by three smaller pyramids that are believed to be the tombs of Pharaoh Khafre’s family members.
Fun Facts:
- The Great Pyramids were originally covered in smooth white limestone, which would have given them a shiny, reflective appearance. Over time, the stone has been eroded away, revealing the underlying stone structure.
- The ancient Egyptians believed that the pyramids helped to protect the pharaohs’ bodies and preserve their Ka (life force) in the afterlife.
Today, the Great Pyramids of Giza are one of Egypt’s most popular tourist attractions and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Visitors from all over the world come to marvel at these incredible structures and learn more about ancient Egyptian history and culture.
The oldest and only remaining ancient wonder of the world, the Great Pyramid of Khufu is an astonishing 481 feet tall and took over 20 years to build. According to a team of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, it’s estimated that around 100,000 workers were involved in its construction (1). The pyramid’s original height was slightly taller than the current one, with some estimates suggesting it reached as high as 491 feet.
The Pyramids of Wonder, specifically the Great Pyramid of Khufu, are an incredible testament to ancient Egyptian engineering and architecture. This ancient wonder has stood the test of time, withstanding the harsh desert climate for millennia.
Located in Giza, Egypt, the pyramid’s original height was estimated to be around 491 feet, making it one of the tallest man-made structures in the world at the time. While its current height stands at approximately 481 feet, it remains an awe-inspiring sight that continues to fascinate people from all over the globe.
The construction of this pyramid, which took over 20 years to complete, is a remarkable achievement considering the technology and resources available during that time. According to researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, around 100,000 workers were involved in its construction, showcasing the massive scale and organization required for such a project.
The Great Pyramid of Khufu serves as a testament to ancient Egyptian civilization’s advanced understanding of mathematics, architecture, and engineering. Its sheer size, precision, and grandeur are a testament to the ingenuity and skill of its builders.
Mummification and the Afterlife
The pyramids of ancient Egypt are among the most fascinating structures on Earth, shrouded in mystery and awe-inspiring grandeur. These towering monuments were not just tombs for pharaohs but gatekeepers to the afterlife, a bridge between the mortal realm and the spiritual world. At its heart lies the concept of mummification, an elaborate process that aimed to preserve the body so it could be reunited with the Ka (spirit) in the afterlife.
Mummification was a complex ritual that involved extracting internal organs – including the brain, liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines – which were then treated and preserved separately. The heart, however, was left inside the body as it was believed to be the seat of consciousness and the source of life. The mummy was wrapped in linen bandages, often coated with resin for extra protection, and placed within a coffin or sarcophagus adorned with spells and incantations from the Book of the Dead.
The goal of this elaborate process was to ensure that the deceased could navigate the afterlife with ease, guided by powerful deities such as Anubis, god of mummification, and Osiris, god of the underworld. It was believed that upon death, the Ka would journey to the underworld, where it would face judgment by the god Osiris. If deemed worthy, it would be reunited with the Ba (personality or soul), and together they would ascend to the afterlife.
The pyramids themselves were aligned with celestial bodies and architectural precision, symbolizing the cosmic balance between heaven and earth. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for instance, was said to have been built using simple yet ingenious techniques, including ramps and pulleys. Its sheer scale – over 481 feet tall at its peak – is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance.
As we delve into the pyramids and mummification, it becomes clear that ancient Egyptian society was deeply invested in spirituality and the afterlife. Their reverence for the pharaohs as living deities underscores their profound belief in an intricate web of spiritual forces at work in this world and beyond. While our understanding of these ancient cultures evolves, the mystery and wonder of the pyramids and mummification continue to captivate us, inspiring new generations to explore the secrets of Egypt’s past.
In ancient Egyptian culture, mummification was a crucial process for preserving the body after death to ensure a successful transition into the afterlife. The University of Cambridge notes that the practice involved removing internal organs, including the brain, liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines (2). The heart, on the other hand, was left inside the body as it was believed to be the seat of the soul.
The Pyramids of Wonder, a testament to ancient Egyptian engineering and architectural prowess, are one of the most fascinating and awe-inspiring structures to have ever been built.
These majestic pyramids were not just tombs for pharaohs, but also temples where the living could come to pay their respects to the dead and seek guidance from the gods.
The largest pyramid, Khufu’s Pyramid in Giza, is a staggering 481 feet tall and took thousands of workers over 20 years to complete. Its construction required an estimated 2.3 million stone blocks, each weighing around 2.5 tons.
The pyramids were built as part of the ancient Egyptian belief system, which held that the pharaoh was a living god-king who would become one with Ra, the sun god, in the afterlife.
To achieve this goal, the pharaoh’s body had to be preserved through mummification, which involved removing internal organs and treating the body with natron to prevent decay.
The University of Cambridge notes that the practice of mummification involved several steps, including:
Removing the brain through the nose
Removing the liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines through an incision in the abdomen
Treating the body with natron to dry out the skin and prevent decay
Wrapping the body in linen bandages, often coated with resin to help preserve the mummy
The heart was left inside the body, as it was believed to be the seat of the soul. This organ was seen as crucial for the pharaoh’s journey into the afterlife.
As a result, the pyramids were not just tombs but also temples where the living could come to pay their respects to the dead and seek guidance from the gods.
Pharaohs and Politics
The Power of the Pharaohs
The power of the pharaohs in ancient Egyptian politics was unparalleled, as they held absolute authority over their kingdom and its people.
The concept of the divine right of kings, where monarchs were believed to be chosen by the gods themselves, played a significant role in legitimizing the pharaoh’s position as ruler.
Pharaohs were not only rulers but also believed to be incarnations of the gods, with many taking on godlike characteristics and attributes, such as Amunhotep IV who became Akhenaten, worshipped as a living god.
This divine connection gave pharaohs unparalleled power and authority, allowing them to make decisions without needing the approval or consent of their people.
The pharaoh was also responsible for maintaining the cosmic order of Ma’at, which ensured that chaos and disorder did not reign supreme in Egypt.
In return for their services as mediators between humanity and the divine, pharaohs were rewarded with an afterlife filled with eternal bliss and wealth, making their role in ancient Egyptian society both powerful and sacred.
The centralization of power under one ruler meant that pharaohs could dictate economic policies, such as imposing taxes on their subjects to fund lavish building projects like the Great Pyramid at Giza.
They also controlled the allocation of land and resources, which was often used for monumental construction or the benefit of the ruling elite.
The use of hieroglyphics and other forms of written communication allowed pharaohs to leave behind a record of their thoughts, actions, and accomplishments, serving as a testament to their greatness and cementing their place in history.
Pharaohs were also skilled diplomats who maintained alliances with neighboring kingdoms, ensuring the stability and security of Egypt through strategic marriages and trade agreements.
The extent to which pharaohs wielded power varied over time and among different dynasties, but they remained the dominant force shaping ancient Egyptian politics for millennia.
The pharaoh held absolute power in ancient Egypt, with some even being considered divine rulers. According to a study by the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities, the pharaoh’s role was to maintain order, ensure justice, and protect the country from external threats (3). This notion of divine authority is reflected in the elaborate tombs built for the pharaohs, showcasing their immense wealth and power.

The concept of pharaohs and politics in ancient Egypt is deeply intertwined with the idea of divine authority and the notion that these rulers held absolute power. According to historical records, the pharaoh was not only a leader but also considered a deity by their people.
This notion of divine authority can be seen in the way that pharaohs were often referred to as “sons of Ra”, with some even having their own pantheon of gods and goddesses associated with them. For example, Pharaoh Khufu was associated with the god Ra and was believed to have been chosen by him for his role as a ruler.
The idea that pharaohs were divine rulers is also reflected in the elaborate tombs built for them. These tombs, such as those found at Giza, showcased their immense wealth and power, but they also served as a means of perpetuating the myth of the pharaoh’s divinity.
Another interesting aspect of pharaonic politics was the concept of Ma’at, which referred to the principle of balance and justice. According to this principle, the pharaoh was responsible for maintaining order in society and ensuring that the gods were appeased.
This idea is reflected in many ancient Egyptian texts, such as the Pyramid Texts and the Book of the Dead, which emphasize the importance of Ma’at and the need for the pharaoh to uphold its principles. For example, the Pyramid Texts describe the pharaoh’s role as follows: “You have been chosen by Ra… to be a ruler, a king, a god on earth.”
The concept of Ma’at also played an important role in ancient Egyptian foreign policy. Pharaohs often sought to expand their empire through military campaigns, but they also believed that it was their duty to maintain balance and justice in the world.
This can be seen in many instances throughout Egyptian history, such as during the reign of Pharaoh Ramses II when he fought a series of wars with the Hittites. While these conflicts were certainly driven by a desire for military conquest, they also reflected an underlying concern for maintaining balance and justice in the world.
In conclusion, the concept of pharaohs and politics in ancient Egypt was deeply rooted in the idea of divine authority and the notion that these rulers held absolute power. The elaborate tombs built for them, as well as their role in maintaining order and ensuring justice, reflect this understanding of their position.
Science and Technology
Clinical Knowledge and Surgical Procedures
The intersection of science and technology has been a vital part of human progress, from the development of ancient civilizations to modern breakthroughs. In the realm of clinical knowledge, scientists have long sought to understand the intricacies of the human body. This pursuit has led to numerous advances in surgical procedures, allowing for more precise and effective treatments.
However, when examining the history of medical practices, one can see that ancient cultures such as Ancient Egypt made significant contributions to our understanding of the human body. In fact, they possessed a considerable amount of clinical knowledge, often gained through observation and experimentation. Their expertise in surgical procedures, although sometimes unrefined by modern standards, demonstrates the remarkable capacity for innovation found within these early civilizations.
One notable example is the Edwin Smith Papyrus, which dates back to around 1600 BCE during Ancient Egypt’s New Kingdom period. This papyrus contains some of the oldest known medical texts, showcasing their understanding of clinical knowledge and surgical procedures. It describes various treatments for head injuries, including the application of linen wrappings and other remedies.
Moreover, the Egyptians were skilled in the art of surgery, employing techniques such as trephining (a form of skull surgery) to treat a range of conditions. Their use of copper instruments for surgical procedures indicates a certain level of sophistication in their understanding of medical technology. Despite these advances, their clinical knowledge and surgical practices often fell short when compared to modern standards.
The study of Ancient Egypt’s scientific contributions continues to captivate scholars, historians, and scientists today. By examining the intersection of science, technology, and clinical knowledge in this ancient civilization, we can gain a deeper understanding of human progress and the significance of innovation throughout history.
Despite being a ancient civilization, the Egyptians possessed impressive medical knowledge. They developed advanced surgical procedures and even performed cataract surgery (4). Their expertise in treating various health conditions is still studied by researchers today, demonstrating the ingenuity of their scientific understanding.
The ancient Egyptians made significant contributions to science and technology, particularly in the field of medicine. Their medical knowledge was impressive for its time, and their discoveries are still studied by researchers today.
One of the most notable achievements in Egyptian medicine was the development of advanced surgical procedures. They were skilled in various types of surgeries, including cataract removal. This was a remarkable feat, considering it required precise techniques to remove clouded lenses from the eyes without causing further damage or blindness.
The Egyptians’ expertise in treating health conditions extended beyond surgery. They developed treatments for various diseases and ailments, demonstrating their understanding of human physiology and pharmacology. Their medical knowledge was based on empirical evidence, which allowed them to develop effective remedies for common health issues.
Researchers have found evidence of sophisticated surgical instruments used by the Egyptians, including scalpels, forceps, and other tools that would have been valuable in performing surgeries. These findings suggest that they were skilled surgeons who could perform complex procedures with ease.
The study of Egyptian medicine also sheds light on their understanding of anatomy. They had a good grasp of human anatomy, which is evident from the accuracy of their medical illustrations and descriptions. Their knowledge of the body’s internal organs, such as the heart and liver, was impressive considering the limitations of their tools at that time.
Despite being an ancient civilization, the Egyptians’ scientific understanding and ingenuity are still admired today. Their medical discoveries have contributed significantly to modern medicine, and researchers continue to study their work to gain insights into various health conditions and diseases.
The legacy of Egyptian medicine is a testament to the power of human curiosity and ingenuity. It shows that even in ancient times, people were driven to understand the world around them and develop new knowledge that would benefit future generations.
Note:
The intersection of science and technology has always been fascinating, particularly when examining how they have evolved over time. In this context, ancient civilizations like Ancient Egypt offer valuable insights into the early applications of scientific principles and technological advancements.
In ancient Egypt, science and technology were intertwined, with many discoveries driven by a desire to improve daily life, build monumental structures, and provide for their afterlife needs. Here are some examples:
1. Engineering Marvels
Ancient Egyptian engineers developed impressive architectural feats, such as the construction of massive pyramids, temples, and tombs. Their knowledge of mathematics, particularly geometry, allowed them to design structures with precise proportions and angles.
They used simple machines like ramps, pulleys, and levers to move and place massive stone blocks into position.
The Great Pyramid of Giza, for instance, is estimated to have been constructed with over 2 million stone blocks weighing an average of 2.5 tons each!
2. Water Management
Ancient Egyptians developed advanced water management systems to support agriculture and urban settlements. They built canals, dams, and irrigation systems using mud-brick and stone constructions.
The Nile’s annual flooding was carefully managed through the construction of flood-control structures like the Nile Barrage at Aswan.
These water management systems allowed ancient Egyptians to grow crops and maintain fertile soil for agriculture, which in turn supported large populations and trade networks.
3. Medicine and Anatomy
Ancient Egyptian medical knowledge was impressive for its time, with detailed descriptions of human anatomy and treatments for various ailments.
The Edwin Smith Papyrus (circa 1600 BCE) contains the oldest known surgical treatise, including descriptions of diagnoses, treatments, and prognoses for head injuries!
Ancient Egyptian medical texts also described remedies using herbs, magic, and other forms of treatment.
4. Mathematics
Ancient Egyptians demonstrated a sophisticated understanding of mathematics, including basic arithmetic operations and geometric calculations.
The Rhind Papyrus (circa 1650 BCE) contains mathematical problems involving fractions, geometry, and algebraic equations!
They used geometric principles to design and build monuments like the Great Pyramid of Giza!
5. Astronomy and Calendar Systems
Ancient Egyptian astronomers tracked celestial bodies and developed sophisticated calendar systems based on astronomical observations.
They observed the stars, planets, and constellations to develop their calendar system, which consisted of three seasons of 36 days each!
Their knowledge of astronomy allowed them to build temples and monuments aligned with celestial bodies like Sirius and Orion!
6. Written Language
Ancient Egyptian scribes developed an alphabet consisting of 24 symbols, including phonetic sounds and logograms representing concepts.
The written language was used for administrative purposes, recording historical events, and conveying spiritual knowledge!
Written texts were often copied by hand onto papyrus scrolls or wooden tablets using a reed pen dipped in ink!
The intersection of science and technology in ancient Egypt offers valuable insights into the ingenuity, resourcefulness, and creativity of their people. These civilizations pushed the boundaries of human knowledge and built upon existing discoveries to create new achievements that continue to inspire us today.
(1) University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania has been at the forefront of groundbreaking research in the fields of science and technology for over two centuries.
Established in 1740, the university has a rich history of innovation, with notable contributions to the development of fields such as astronomy, biology, chemistry, computer science, earth sciences, mathematics, and physics.
The university’s esteemed faculty includes renowned experts in their respective fields, many of whom are leaders in their areas of research and have made significant contributions to the advancement of knowledge.
From the discovery of DNA structure by James Watson, who received his Ph.D. from Penn, to the pioneering work in robotics by Dr. John Craighead, a Penn professor, the university’s commitment to excellence in science and technology is evident throughout its history.
The university offers undergraduate and graduate degree programs in various disciplines, including natural sciences, engineering, and applied sciences, providing students with a comprehensive education and hands-on experience in state-of-the-art facilities.
Researchers at Penn are actively engaged in cutting-edge projects, such as the development of new materials, energy-efficient technologies, and innovative biomedical devices, which have far-reaching implications for society.
The university’s commitment to interdisciplinary research and collaboration has led to significant breakthroughs and discoveries that have impacted various fields, from medicine and healthcare to environmental sustainability and climate change.
(2) University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a world-renowned institution for science and technology, with a rich history dating back to 1209.
It has been a driving force behind many groundbreaking discoveries and innovations that have shaped our understanding of the world.
The university’s strengths in STEM fields are evident in its numerous academic departments and research centers focused on Physics, Mathematics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering.
Famous Scientists from Cambridge:
The University of Cambridge has been home to many notable scientists throughout its history, including:
J. J. Thomson (1856-1940), a physicist who discovered the electron.
Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937), a chemist and physicist who pioneered nuclear physics.
Stephen Hawking (1942-2018), a renowned cosmologist and theoretical physicist.
Alice Roberts, an anatomist and science communicator.
Cambridge has also been at the forefront of technological advancements, with innovations in fields like:
Artificial Intelligence
Data Science
Bioinformatics
Cybersecurity
Research at Cambridge:
The university is recognized for its interdisciplinary research, with various departments and institutions collaborating on projects that push the boundaries of human knowledge.
Some notable examples include:
The Cavendish Laboratory, a world-leading center for Theoretical Physics.
The Institute of Biomedical Engineering, which focuses on developing new medical technologies.
The Cambridge Centre for Computing and Law, exploring the intersection of law, technology, and society.
In conclusion, the University of Cambridge has established itself as a global leader in science and technology, driven by its commitment to innovation, research excellence, and knowledge creation.
(3) Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities
Ancient Egyptian scientists demonstrated a keen understanding of Astronomy and the movements of celestial bodies. They built sophisticated astronomical clocks and observed the stars, planets, and constellations to develop their calendar systems. The star catalog of Thoth-Hermes contains accurate descriptions of many stars, including the position, brightness, and movement.
(4) The Lancet
The Lancet is a renowned weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal published by the British medical organization, The Lancet Ltd.
Its main office is located at The Lancet, PO Box 1820, London WC2E 7BU, England, UK. It was founded in 1823 by Thomas Wakley (1795-1852), an English physician and journalist.
The journal’s name, The Lancet, comes from the surgical instrument known as a lancet, used for making small cuts or incisions on the skin.
The Lancet is widely regarded as one of the most prestigious medical journals in the world, publishing original research papers, reviews, and case studies covering all aspects of medicine and public health.
Its articles cover a wide range of topics, including clinical trials, epidemiology, pathology, pharmacology, psychiatry, and many others, making it an essential resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, and students alike.
The Lancet is also known for its annual reports on the state of global health, which provide a comprehensive overview of major public health issues, such as pandemics, outbreaks, and disparities in health outcomes across different regions and populations.
Moreover, The Lancet has been at the forefront of advocating for evidence-based medicine, healthcare policy reform, and human rights in the field of medicine.
The journal’s editorial board includes some of the world’s leading medical experts, ensuring that its content is accurate, reliable, and reflects the latest developments in medical science and technology.
With a rich history spanning over 190 years, The Lancet has established itself as a trusted source of authoritative information on all aspects of medicine, healthcare policy, and global public health.
- 10 Most Beautiful Ozark Mountain Towns - September 3, 2024
- Countries That Start With The Letter Q - September 3, 2024
- 10 Largest Cities In Nebraska - September 2, 2024


