Introduction to Eurasia
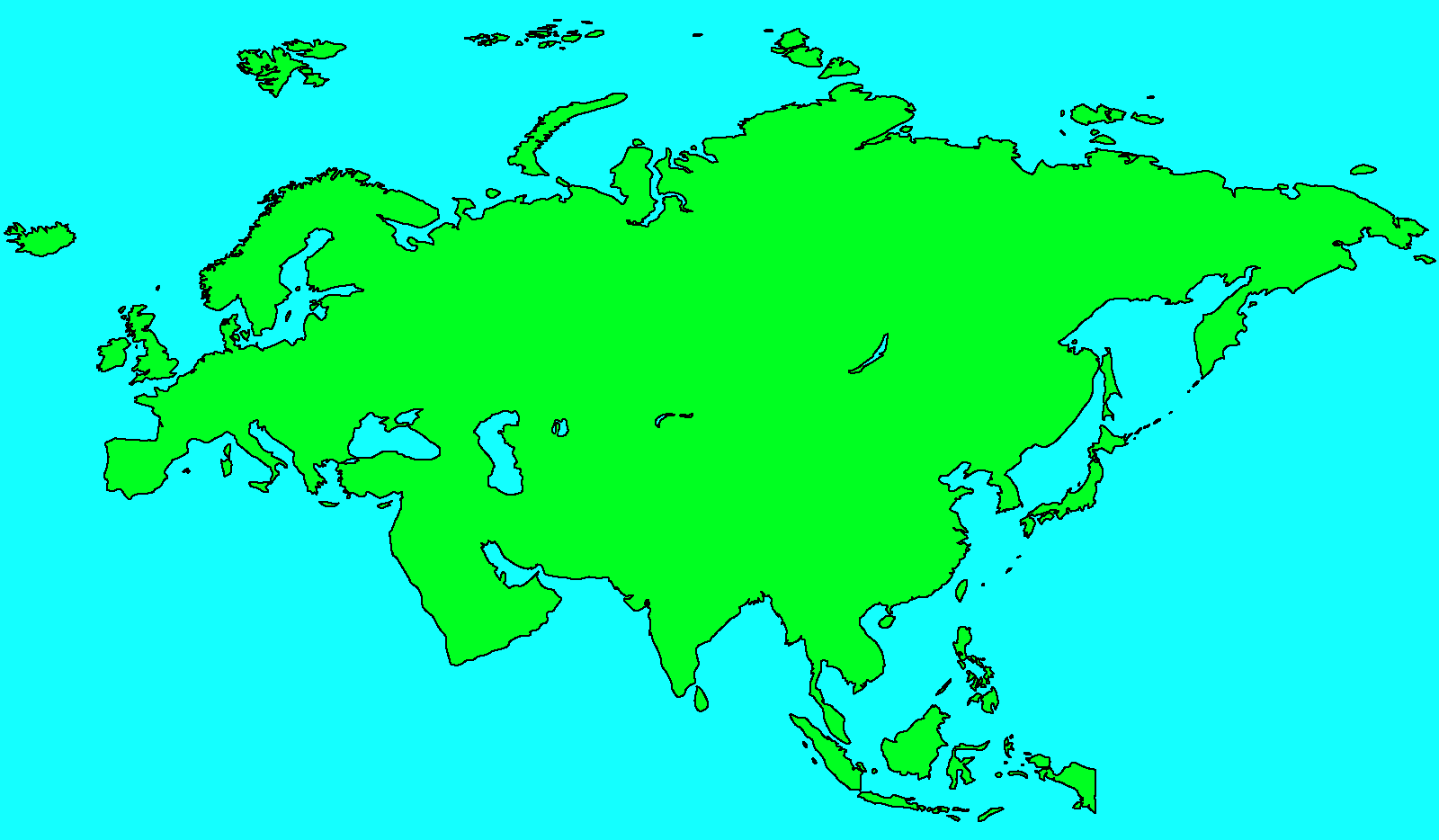
Eurasia is the combined continental landmass of Europe and Asia, covering approximately 55 million square kilometers. It stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, forming a bridge between two continents.
Geography of Eurasia
Location and Boundaries
- Eurasia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Pacific Ocean to the east.
- It includes diverse geographical features such as mountains (e.g., the Ural Mountains), plains (e.g., the Eurasian Steppe), and major rivers (e.g., the Volga and Yangtze).
Subregions
- Europe, located west of the Ural Mountains, is known for its cultural diversity, historical landmarks, and industrialized economies.
- Asia, east of the Ural Mountains, is characterized by vast expanses of wilderness, ancient civilizations, and emerging economies.
History and Culture
Historical Significance
- Eurasia has been a cradle of civilization, hosting ancient cultures such as Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilization, and the Silk Road trade route.
- It has witnessed significant historical events, including the rise and fall of empires like the Roman Empire, Mongol Empire, and Soviet Union.
Cultural Diversity
- Eurasia is home to diverse ethnic groups, languages, and religions, contributing to its rich cultural tapestry.
- It showcases architectural marvels like the Kremlin in Moscow, the Great Wall of China, and the Acropolis in Athens.
Economy and Trade
Economic Powerhouses
- Eurasia includes some of the world’s largest economies, including Russia, China, Germany, and India.
- It serves as a hub for international trade, connecting Europe and Asia through the Trans-Siberian Railway, Suez Canal, and Eurasian Economic Union.
Natural Resources
- Eurasia is abundant in natural resources such as oil, natural gas, minerals, and fertile agricultural lands.
- The region’s resource wealth plays a critical role in global energy security and economic stability.
Political and Geopolitical Dynamics
Global Influence
- Eurasia’s geopolitical importance is underscored by its strategic location, economic influence, and military capabilities.
- It is a focal point for international relations, with issues ranging from territorial disputes (e.g., Crimea) to regional cooperation (e.g., Shanghai Cooperation Organization).
Integration Efforts
- Initiatives like the European Union (EU), Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) aim to foster economic integration and cooperation across Eurasian countries.
- Geopolitical tensions, however, also shape dynamics, including conflicts in the Middle East, disputes over natural resources, and strategic military alliances.
Environmental Challenges
Environmental Diversity
- Eurasia’s diverse ecosystems range from Arctic tundra and boreal forests to tropical rainforests and deserts.
- Climate change poses significant challenges, affecting glaciers, permafrost, and biodiversity across the continent.
Tourism and Cultural Heritage
Tourist Attractions
- Eurasia boasts iconic landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Taj Mahal, Kremlin, and Petra.
- It offers diverse travel experiences, from exploring ancient ruins in Greece to trekking the Himalayas in Nepal.
Cultural Interactions
- Eurasia’s cultural exchanges through trade, migration, and diplomacy have shaped global history and fostered cross-cultural understanding.
- Festivals, cuisine, and traditions reflect the region’s rich heritage and influence on global arts and entertainment.
Conclusion
Eurasia stands as a testament to human civilization’s evolution, from ancient civilizations to modern economic powerhouses. Its vast landscapes, cultural diversity, and geopolitical significance continue to shape global dynamics and inspire exploration. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of Eurasia’s geography, history, culture, economy, and challenges, highlighting its role as a bridge between continents and a cradle of human innovation.
What is Eurasia also known as?
Eurasia is also known as the “Eurasian continent,” encompassing both Europe and Asia.
What is a fact about Eurasia?
Eurasia is the largest continental landmass on Earth, spanning approximately 55 million square kilometers.
Which two continents are from Eurasia?
Eurasia comprises Europe and Asia, connected by the Ural Mountains and separated by the Ural River and Caspian Sea.
What is Eurasia divided by?
Eurasia is traditionally divided by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and Black Sea.
How large is Eurasia?
Eurasia covers about 36.2% of the Earth’s total land area, making it the largest contiguous landmass.
What is the largest country in Europe?
Russia is the largest country in Europe by land area, spanning across both Europe and Asia.
Why is Eurasia not one continent?
Eurasia is considered two continents due to historical, cultural, and geological distinctions between Europe and Asia, despite being connected geographically.
What does Eurasian mean?
“Eurasian” refers to something or someone related to Eurasia, typically describing cultural, ethnic, or geographical connections between Europe and Asia.
What is the full form of Eurasian?
There is no specific full form for “Eurasian.” It directly refers to the combined landmass of Europe and Asia.
What language is Eurasia?
Eurasia is not a language but rather a geographical term referring to the combined landmass of Europe and Asia.
- The Largest Lizards In The World - September 9, 2024
- Taos, New Mexico - September 9, 2024
- The Most Colorful Birds From Around The World - September 9, 2024