Introduction to Ecuador
Geographic Overview
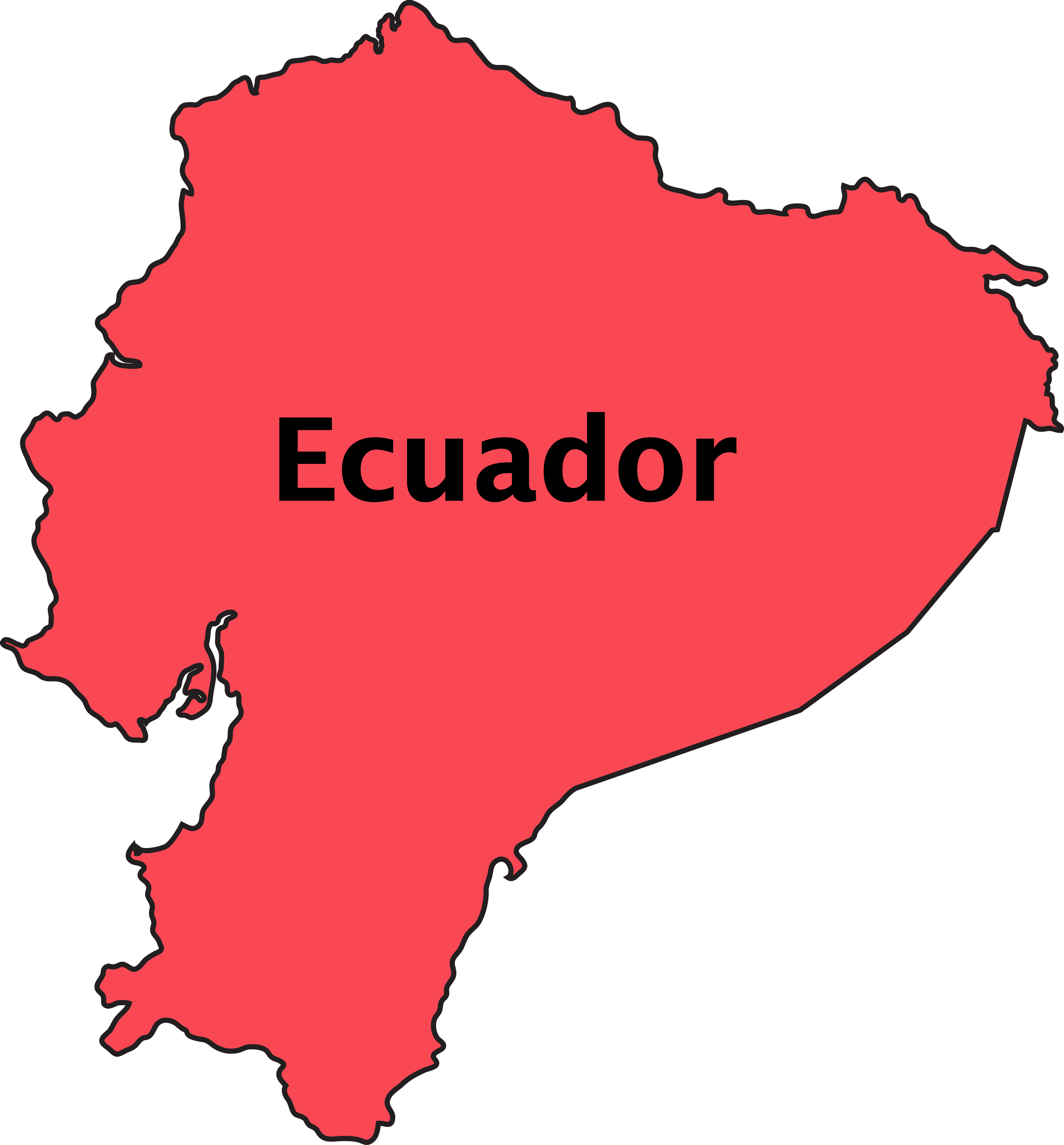
Ecuador is situated on the northwestern coast of South America, bordered by Colombia to the north, Peru to the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Despite its relatively small size, Ecuador is renowned for its remarkable geographical diversity, encompassing coastal plains, Andean highlands, and the Amazon rainforest.
Fun Fact
Ecuador is one of the 17 megadiverse countries in the world, boasting an incredible array of wildlife and plant species.
Historical Context
Ecuador has a rich history, from ancient indigenous civilizations to Spanish colonization and eventual independence in 1822. Its historical journey has significantly influenced its cultural and social landscape.
Ecuador Maps
Political Map
A political map of Ecuador highlights its administrative divisions, including provinces, major cities, and important geographical features.
- Provinces: Ecuador is divided into 24 provinces, each with its own capital and administrative structure.
- Major Cities: The capital city is Quito, while other significant cities include Guayaquil, Cuenca, and Ambato.
Physical Map
A physical map showcases Ecuador’s diverse topography, including
- The Coastal Plain (La Costa): A lowland area adjacent to the Pacific Ocean, known for its fertile land and agricultural productivity.
- The Andean Highlands (La Sierra): Home to the Andes Mountains, this region features high altitudes, volcanic peaks, and vibrant indigenous cultures.
- The Amazon Rainforest (El Oriente): This eastern region encompasses dense rainforest, rich biodiversity, and numerous indigenous communities.
The Galápagos Islands
Located about 1,000 kilometers off the Ecuadorian coast, the Galápagos Islands are a province of Ecuador and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. They are famous for their unique flora and fauna, which significantly contributed to Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution.
Climate Map
Ecuador’s climate is highly variable due to its geographical diversity and altitude variations
- Coastal Region: Tropical climate with a wet season from December to May.
- Highlands: Temperate climate with mild temperatures year-round.
- Amazon Basin: Humid and tropical with significant rainfall throughout the year.
- Galápagos Islands: Dry climate with warm temperatures year-round.
Geographic Features
Andean Mountains
The Andes Mountains run north to south through Ecuador, forming the backbone of the country. Notable peaks include
- Mount Chimborazo: The highest peak in Ecuador and the point on Earth closest to the sun due to the equatorial bulge.
- Cotopaxi: One of the world’s highest active volcanoes, a prominent feature of the Andean landscape.
Amazon Rainforest
The Ecuadorian Amazon is part of the larger Amazon Basin and is renowned for its biodiversity. Key features include
- Yasuni National Park: One of the most biologically diverse places on Earth.
- Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve: Known for its diverse wildlife, including river dolphins, anacondas, and hundreds of bird species.
Coastal Region
Ecuador’s coastline is dotted with beautiful beaches, mangroves, and rich fishing grounds. Key coastal features include:
- Machalilla National Park: Home to diverse ecosystems including dry forests, beaches, and the Isla de la Plata, often called a “mini-Galápagos.”
Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands are a volcanic archipelago renowned for their unique species and ecosystems. Notable islands include:
- Isabela Island: The largest island, home to the Sierra Negra volcano.
- Santa Cruz Island: Location of the Charles Darwin Research Station.
Political Divisions
Provinces and Capitals
Ecuador’s administrative structure is divided into 24 provinces, each governed by a provincial government. Some notable provinces include:
- Pichincha: Capital is Quito, the national capital.
- Guayas: Capital is Guayaquil, the largest city and economic hub.
- Azuay: Capital is Cuenca, known for its colonial architecture and cultural heritage.
Autonomous Regions
Ecuador recognizes certain indigenous territories with a degree of autonomy, allowing for the preservation of indigenous cultures and governance systems.
Major Cities
Quito
Quito is the capital city and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, known for its well-preserved historic center. Key attractions include:
- Plaza Grande: The main square surrounded by significant buildings such as the Presidential Palace.
- Basilica del Voto Nacional: An impressive neo-Gothic church with stunning city views from its towers.
Guayaquil
Guayaquil is Ecuador’s largest city and main port. It is a vibrant economic center with attractions like
- Malecón 2000: A revitalized waterfront area with parks, museums, and restaurants.
- Las Peñas: A historic neighborhood with colorful houses and art galleries.
Cuenca
Cuenca is known for its colonial architecture, cultural festivals, and artisan crafts. Notable landmarks include
- New Cathedral of Cuenca: A striking cathedral with distinctive blue domes.
- Tomebamba River: A picturesque river that runs through the city.
Other Significant Cities
- Ambato: Known for its festivals and agricultural produce.
- Loja: A cultural hub in southern Ecuador, famous for its music and arts scene.
Natural Wonders
Amazon Rainforest
Ecuador’s Amazon region is a biodiversity hotspot. Key attractions include
- Napo Wildlife Center: A community-run ecotourism project offering wildlife viewing and cultural experiences.
- Yasuni Biosphere Reserve: Home to incredible biodiversity and indigenous communities.
Andean Highlands
The Andean region offers breathtaking landscapes and outdoor activities
- Avenue of the Volcanoes: A stretch of the Andes with numerous volcanoes, ideal for trekking and mountaineering.
- Laguna Quilotoa: A stunning crater lake popular for hiking and photography.
Coastal Region
Ecuador’s coast boasts beautiful beaches and marine life
- Montañita: A renowned surf spot and vibrant beach town.
- Puerto López: Gateway to Machalilla National Park and whale watching tours.
Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos are a natural wonder, famous for their unique wildlife and ecosystems. Highlights include
- Giant Tortoises: Found on several islands, these iconic creatures are a symbol of the Galápagos.
- Marine Iguanas: Unique to the Galápagos, these iguanas are the only marine lizards in the world.
Cultural Highlights
Indigenous Cultures
Ecuador is home to numerous indigenous groups, each with distinct languages, traditions, and customs. Key cultural aspects include
- Otavalo Market: One of the largest indigenous markets in South America, known for its textiles and crafts.
- Inti Raymi Festival: An important Andean celebration of the winter solstice, held in various indigenous communities.
Colonial Heritage
Ecuador’s colonial history is evident in its architecture, festivals, and cultural practices
- Quito’s Historic Center: A UNESCO World Heritage Site with well-preserved colonial buildings.
- Fiestas de Quito: Annual celebrations in honor of Quito’s foundation, featuring parades, music, and traditional dances.
Modern Culture
Ecuador’s contemporary culture is a blend of indigenous, colonial, and modern influences. Key elements include
- Music and Dance: Ecuadorian music ranges from traditional Andean rhythms to modern pop and reggaeton.
- Cuisine: Ecuadorian cuisine is diverse, with regional specialties such as ceviche, empanadas, and llapingachos.
What is the capital of Ecuador?
The capital of Ecuador is Quito, known for its high altitude and well-preserved historic center.
What is Ecuador known for?
Ecuador is known for its incredible biodiversity, the Galápagos Islands, Andean landscapes, and rich cultural heritage.
How many provinces are there in Ecuador?
Ecuador is divided into 24 provinces, each with its own administrative capital.
What languages are spoken in Ecuador?
The official language of Ecuador is Spanish, but several indigenous languages, including Quechua and Shuar, are also widely spoken.
What is the climate like in Ecuador?
Ecuador’s climate varies by region: the coastal area has a tropical climate, the highlands have a temperate climate, the Amazon basin is humid and tropical, and the Galápagos Islands have a dry climate.
What are some popular tourist destinations in Ecuador?
Popular tourist destinations in Ecuador include Quito, Guayaquil, the Galápagos Islands, Cuenca, and the Amazon Rainforest.
What is the significance of the Galápagos Islands?
The Galápagos Islands are significant for their unique wildlife and ecosystems, which contributed to Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution.
How does Ecuador’s geography influence its culture?
Ecuador’s geography, with its diverse regions, influences its culture by contributing to varied lifestyles, traditions, and cuisines across different parts of the country.
What is Ecuador’s main export?
Ecuador’s main exports include petroleum, bananas, shrimp, and flowers.
Are there any UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Ecuador?
Yes, Ecuador is home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including Quito’s historic center, the Galápagos Islands, and Sangay National Park.
Conclusion
Ecuador is a country of remarkable diversity, from its stunning natural landscapes to its rich cultural heritage. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at Ecuador’s maps and facts, highlighting its geographical features, political divisions, major cities, and cultural highlights. Whether you are interested in exploring its Andean peaks, Amazonian rainforests, or vibrant cities, Ecuador offers a wealth of experiences for visitors and residents alike.
- 5 Marsupials Who Aren’t Kangaroos - October 4, 2024
- 20 Interesting Names For Groups Of Animals - October 3, 2024
- 15 Largest Peninsulas In The World - October 3, 2024