Introduction to Switzerland
Switzerland is a landlocked country bordered by Germany to the north, France to the west, Italy to the south, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Despite its small size, Switzerland has a significant influence on global politics, economics, and culture. Known for its policy of neutrality, Switzerland is home to numerous international organizations, including the Red Cross and several United Nations agencies.
Geography of Switzerland
Switzerland is divided into three main geographical regions: the Swiss Plateau, the Jura Mountains, and the Swiss Alps.
Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau, also known as the Central Plateau, is the most densely populated region of Switzerland. It stretches from Lake Geneva in the west to Lake Constance in the east and is characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and numerous lakes. The plateau is home to major cities such as Zurich, Geneva, and Bern, the capital city.
Jura Mountains
The Jura Mountains form the natural border between Switzerland and France. This region is known for its rugged terrain, dense forests, and karst topography, which includes limestone caves and underground rivers. The Jura is less populated than the plateau but offers stunning landscapes and numerous opportunities for outdoor activities like hiking, skiing, and caving.
Swiss Alps
The Swiss Alps are perhaps the most famous geographical feature of Switzerland. This mountainous region covers approximately 60% of the country’s total land area and includes some of the highest peaks in Europe, such as the Matterhorn, Dufourspitze, and Eiger. The Alps are a major tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year for skiing, mountaineering, and enjoying the breathtaking scenery.
Climate of Switzerland
Switzerland’s climate varies significantly depending on the region and altitude. The Swiss Plateau enjoys a temperate climate with four distinct seasons, including mild winters and warm summers. The Jura Mountains and the Alps experience a more alpine climate, with colder winters, heavier snowfall, and cooler summers.
Regional Climate Variations
- Northern Switzerland: Influenced by the Atlantic, this region has moderate temperatures and relatively high rainfall throughout the year.
- Southern Switzerland: The Ticino region, south of the Alps, experiences a Mediterranean climate with warmer temperatures and less rainfall.
- High Altitudes: The mountainous regions have a colder climate, with temperatures decreasing and snowfall increasing with altitude.
History of Switzerland
Switzerland’s history is marked by its unique position in Europe and its tradition of neutrality and independence.
Early History
The area now known as Switzerland has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The Celts were the dominant group in the region before it became part of the Roman Empire in 58 BC. After the fall of Rome, the area was invaded by various Germanic tribes, including the Alemanni and the Burgundians.
Formation of the Swiss Confederation
The Swiss Confederation was established on August 1, 1291, with the signing of the Federal Charter by the three founding cantons of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden. This date is now celebrated as Swiss National Day. The confederation gradually expanded to include other cantons and regions, achieving independence from the Holy Roman Empire in 1648 with the Treaty of Westphalia.
Modern History
In 1848, Switzerland adopted a new constitution that transformed it into a federal state with a strong central government. The country remained neutral during both World Wars and has not been involved in any military conflict since 1815. Today, Switzerland is known for its direct democracy, stable political system, and prosperous economy.
Political System
Switzerland is a federal republic composed of 26 cantons, each with a high degree of autonomy. The Swiss political system is characterized by direct democracy, allowing citizens to participate in decision-making processes through referendums and initiatives.
Federal Government
The federal government is divided into three branches:
- Executive: The Federal Council, a seven-member executive body, functions as the collective head of state and government.
- Legislative: The Federal Assembly, composed of the National Council and the Council of States, is responsible for making federal laws.
- Judicial: The Federal Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority, ensuring the application and interpretation of federal laws.
Cantonal and Municipal Governments
Each canton has its own constitution, government, parliament, and courts. Municipalities also enjoy a significant level of self-governance, managing local affairs and services.
Economy of Switzerland
Switzerland boasts one of the most advanced and stable economies in the world. It is characterized by a high standard of living, low unemployment, and a strong industrial and financial sector.
Key Industries
Finance
Switzerland is renowned for its banking and financial services, with Zurich and Geneva serving as major global financial centers.
Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals:
The country is home to leading pharmaceutical companies like Novartis and Roche, contributing significantly to its GDP.
Manufacturing
Precision manufacturing, including machinery, watches, and instruments, is a crucial part of the Swiss economy.
Tourism
The stunning landscapes and well-developed tourism infrastructure attract millions of visitors annually, making tourism a vital industry.
Trade and Exports
Switzerland has a highly developed export sector, with major exports including pharmaceuticals, machinery, chemicals, and watches. Its main trading partners are the European Union, the United States, and China.
Culture of Switzerland
Switzerland’s culture is a rich tapestry influenced by its linguistic diversity and historical traditions.
Languages
Switzerland has four official languages: German, French, Italian, and Romansh. The linguistic distribution reflects the country’s geographical regions:
- German: Spoken by approximately 63% of the population, predominantly in central and eastern Switzerland.
- French: Spoken by about 23% of the population, mainly in the western part of the country.
- Italian: Spoken by around 8% of the population, primarily in the southern canton of Ticino.
- Romansh: Spoken by less than 1% of the population, mainly in the canton of Graubünden.
Festivals and Traditions
Switzerland hosts numerous festivals and cultural events throughout the year, celebrating its diverse heritage. Some notable festivals include:
- Fasnacht: A lively carnival celebrated in Basel, Lucerne, and other cities.
- Montreux Jazz Festival: One of the world’s most prestigious music festivals, held annually in Montreux.
- Fête de l’Escalade: A historical celebration in Geneva, commemorating the city’s defense against an invasion in 1602.
Cuisine
Swiss cuisine reflects the country’s cultural diversity, with regional dishes influenced by neighboring countries. Some traditional Swiss foods include:
- Fondue: A melted cheese dish served with bread.
- Raclette: Melted cheese served with boiled potatoes and pickles.
- Rösti: A potato dish similar to hash browns, often served as a side dish.
- Chocolate: Switzerland is famous for its high-quality chocolate, with many renowned chocolate brands.
Major Cities and Landmarks
Zurich
Zurich is Switzerland’s largest city and a global financial hub. Known for its vibrant cultural scene, Zurich offers a blend of modernity and tradition, with historical sites such as the Grossmünster and the Bahnhofstrasse shopping street.
Geneva
Geneva is home to numerous international organizations, including the United Nations and the Red Cross. The city is known for its beautiful setting on Lake Geneva, the Jet d’Eau fountain, and its rich cultural heritage.
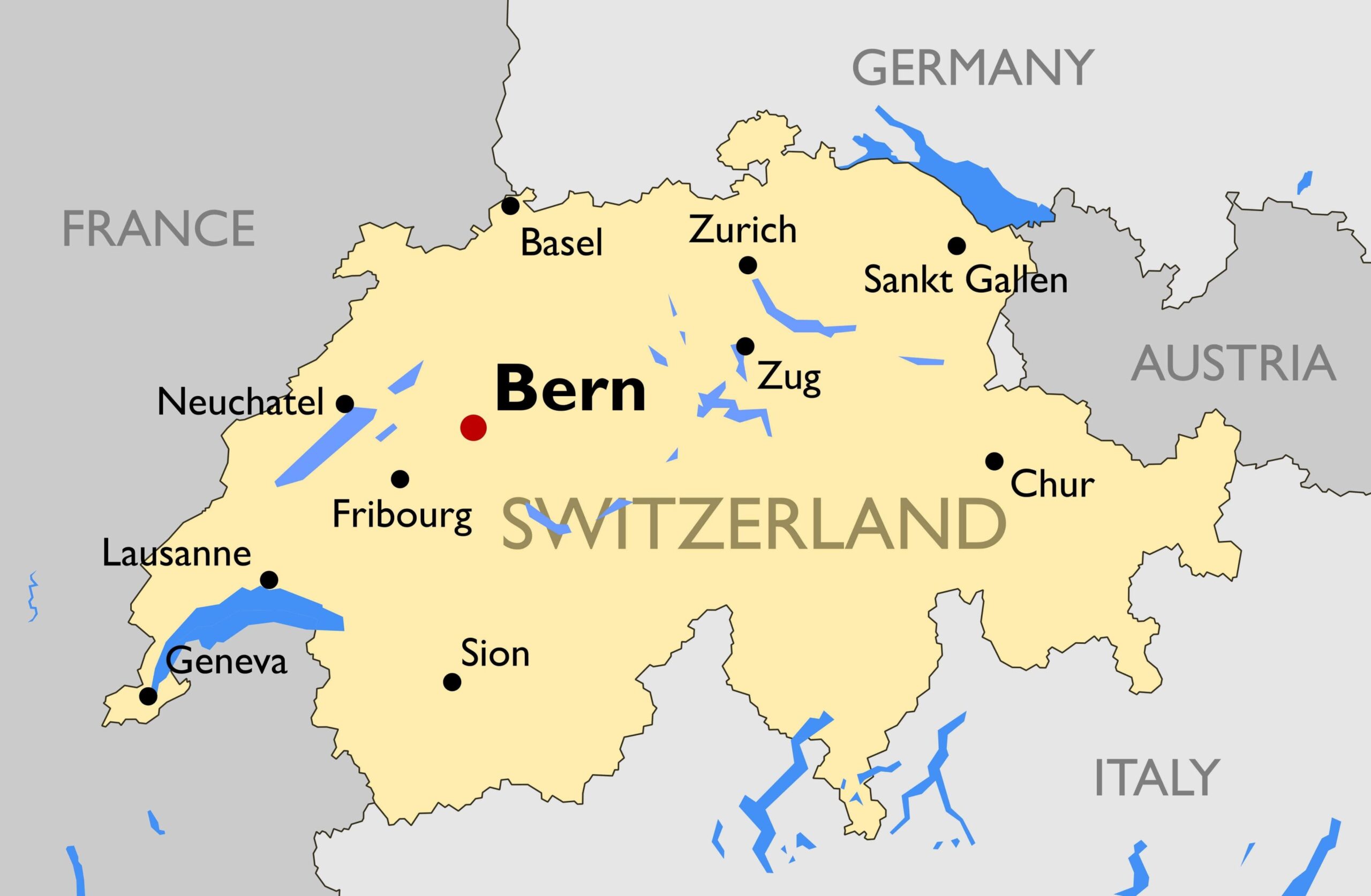
Bern
Bern, the capital city, boasts a well-preserved medieval old town, a UNESCO World Heritage site. The city is known for its Zytglogge clock tower, the Federal Palace, and the Bear Park.
Lucerne
Lucerne, situated on the shores of Lake Lucerne and surrounded by mountains, is famous for its Chapel Bridge, Water Tower, and the Lion Monument. The city is a gateway to the central Swiss Alps.
Interlaken
Interlaken, nestled between Lake Thun and Lake Brienz, is a popular tourist destination for outdoor activities like hiking, skiing, and paragliding. The town offers stunning views of the Jungfrau, Eiger, and Mönch peaks.
Maps of Switzerland
Maps are essential tools for understanding the geographical and cultural landscape of Switzerland. Here are some key maps that provide valuable insights into the country’s features.
Political Map
A political map of Switzerland shows the 26 cantons, each with its boundaries and capital. It highlights major cities, towns, and administrative divisions.
Physical Map
A physical map of Switzerland illustrates the diverse terrain, including the Swiss Alps, Jura Mountains, and the Swiss Plateau. It highlights rivers, lakes, and significant peaks.
Transportation Map
A transportation map of Switzerland shows the extensive network of roads, railways, and airports. Switzerland’s public transportation system is highly efficient, with frequent trains, buses, and boats connecting various regions.
Tourist Map
A tourist map of Switzerland highlights key attractions, landmarks, and scenic routes. It is a useful tool for planning travel itineraries and exploring the country’s rich cultural and natural heritage.
Fun and Interesting Facts about Switzerland
- Neutrality: Switzerland has maintained a policy of neutrality since 1815 and has not participated in any military conflict since then.
- Direct Democracy: Swiss citizens have the right to propose and vote on referendums, allowing them to directly influence laws and policies.
- Chocolate Consumption: Switzerland is one of the largest consumers of chocolate per capita, with Swiss chocolate being renowned worldwide for its quality.
- High Peaks: Switzerland is home to 48 mountains that are 4,000 meters or higher, making it a paradise for mountaineers and hikers.
- Banking Secrecy: Swiss banks are famous for their privacy and security, although banking secrecy has been reduced in recent years to combat tax evasion.
Conclusion
Switzerland is a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and economic prosperity. Its stunning landscapes, efficient public services, and rich history make it a fascinating country to explore. Whether you are interested in its geography, political system, or cultural traditions, Switzerland offers a wealth of information and experiences. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at Switzerland, helping you understand and appreciate this remarkable country.
Commonly Asked Questions about Switzerland
What continent is Switzerland in?
Switzerland is located in Europe, specifically in the central part of the continent.
What is Switzerland known for geographically?
Switzerland is known for its diverse geography, including the Swiss Alps, Jura Mountains, and numerous lakes such as Lake Geneva, Lake Constance, and Lake Zurich.
What is Switzerland called the land of?
Switzerland is often called the “Land of the Alps” due to the significant portion of its territory covered by the Alpine mountain range.
What is the largest city in Switzerland?
The largest city in Switzerland is Zurich, which is a major financial and cultural center.
What is the main city of Switzerland?
The main city, in terms of political significance, is Bern, which serves as the capital of Switzerland.
Which city is most visited in Switzerland?
Zurich is the most visited city in Switzerland, attracting tourists with its historical sites, shopping districts, and beautiful lakeside setting.
What is Switzerland’s capital?
Switzerland’s capital is Bern, known for its medieval old town and status as the political center of the country.
What is Switzerland famous for?
Switzerland is famous for its neutrality, high quality of life, precision engineering (particularly watches), chocolates, banking system, and breathtaking natural landscapes.
What is the nickname of Switzerland?
Switzerland is often referred to as the “Helvetic Confederation” or simply “Helvetia,” based on its Latin name “Confoederatio Helvetica.”
- The Real History Behind The Archimedes Dial Featured In Indiana Jones! - August 19, 2024
- The March Of The 10,000 Greek Hoplites! - August 19, 2024
- Succession Of The Roman Empire! - August 17, 2024