Introduction
Georgia is a country located at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, with a rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes. This comprehensive guide delves into the geography, history, and key facts about Georgia, providing an in-depth understanding of this unique nation.
Overview of Georgia
Georgia, a country in the Caucasus region, is bordered by Russia to the north, Azerbaijan to the southeast, Armenia to the south, and Turkey to the southwest. It also has a coastline along the Black Sea to the west. Georgia’s strategic location has historically made it a point of contention among various empires and a melting pot of cultures and traditions.
Geographical Location
Georgia is situated at the juncture of Europe and Asia, often described as a Eurasian country. The country’s geographic coordinates are approximately 42.3154° N latitude and 43.3569° E longitude. It covers a total area of about 69,700 square kilometers (26,911 square miles).
Topography
Georgia’s topography is highly varied, ranging from coastal regions to mountainous terrains. The country is divided into several distinct geographic regions:
- The Greater Caucasus Mountains: These form the northern boundary of Georgia, featuring some of the highest peaks in Europe, including Mount Shkhara (5,193 meters) and Mount Kazbek (5,047 meters).
- The Lesser Caucasus Mountains: Located in the south, these mountains are lower but still significant in height.
- The Colchis Lowland: Situated along the Black Sea coast, this area is known for its subtropical climate and fertile soils.
- The Kartli Plain: An important agricultural region in central Georgia.
- The Javakheti Plateau: Found in the southern part of the country, this plateau is characterized by volcanic landscapes.
Climate
Georgia experiences a diverse climate due to its varied topography. The climate ranges from subtropical in the coastal areas to continental in the interior regions:
- Western Georgia: Features a humid subtropical climate with heavy rainfall, especially in the Colchis Lowland.
- Eastern Georgia: Exhibits a more continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Mountainous Regions: The Greater and Lesser Caucasus Mountains have alpine climates with significant snowfall during the winter months.
Historical Background
Georgia has a rich and complex history that spans several millennia. The region has been inhabited since ancient times, and its history is marked by periods of independence and foreign domination.
Ancient and Medieval Periods
Early History
The earliest evidence of human habitation in Georgia dates back to the Paleolithic era. The region was later home to the ancient kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia.
Christianization
In the early 4th century, Georgia became one of the first countries to adopt Christianity as its state religion, a move that significantly shaped its cultural and political development.
Golden Age
The 11th to 13th centuries are often considered Georgia’s Golden Age, marked by the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar, who expanded the kingdom and fostered a flourishing of arts and culture.
Modern History
Russian Rule
In the 19th century, Georgia was annexed by the Russian Empire. It briefly gained independence after the Russian Revolution but was soon incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1921.
Independence
Georgia declared independence from the Soviet Union on April 9, 1991. The post-independence period was marked by political instability and economic challenges.
Recent Developments
Since the early 2000s, Georgia has undertaken significant political and economic reforms, seeking closer integration with Western institutions such as the European Union and NATO.
Political Structure and Government
Georgia is a democratic republic with a mixed parliamentary-presidential system. The political structure is defined by the Constitution of Georgia, which was adopted in 1995 and has been amended several times since.
Executive Branch
The executive branch is headed by the President, who serves as the head of state, and the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The President is elected for a six-year term, while the Prime Minister is appointed by the President with the approval of the Parliament.
Legislative Branch
The legislative authority is vested in the Parliament of Georgia, a unicameral body consisting of 150 members. Members of Parliament are elected through a mixed electoral system, combining proportional representation and majoritarian constituencies. The Parliament is responsible for enacting laws, approving the budget, and overseeing the executive branch.
Judicial Branch
The judiciary in Georgia is independent and is tasked with upholding the rule of law. The judicial system includes:
- Constitutional Court: Ensures the constitutionality of laws and acts of government.
- Supreme Court: The highest appellate court in the country.
- Common Courts: Include regional, district, and appellate courts that handle civil, criminal, and administrative cases.
Economy and Infrastructure
Georgia’s economy has undergone significant transformation since the early 2000s, moving from a state-controlled system to a market-oriented economy.
Key Economic Sectors
- Agriculture: Agriculture remains an important sector, employing a significant portion of the population. Key products include wine, nuts, fruits, and vegetables.
- Tourism: Tourism has become a major contributor to the economy, with visitors attracted by Georgia’s natural beauty, historical sites, and cultural heritage.
- Industry: Key industries include mining (especially manganese), manufacturing, and energy.
- Services: The services sector, particularly banking, finance, and IT, has seen rapid growth in recent years.
Infrastructure Development
Georgia has invested heavily in infrastructure development to support economic growth and regional connectivity. Key projects include:
- Transportation: Development of road and rail networks, including the East-West Highway and modernization of the Georgian Railway.
- Energy: Expansion of hydroelectric power and integration into regional energy markets.
- Telecommunications: Rapid growth in the IT sector and widespread availability of internet services.
Culture and Society
Georgia’s culture is a unique blend of influences from Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, reflecting its historical interactions with various civilizations.
Language
The official language of Georgia is Georgian, a Kartvelian language with its own unique script. Georgian is one of the oldest continuously spoken languages in the world. Several other languages, including Russian, Armenian, and Azerbaijani, are also spoken by minority communities.
Religion
The predominant religion in Georgia is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with the Georgian Orthodox Church playing a significant role in national identity. There are also small communities of Muslims, Catholics, and Jews.
Traditions and Festivals
- Polyphonic Singing: Georgian polyphonic singing, recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage, is a significant aspect of the country’s cultural identity.
- Feasts (Supra): The Georgian supra is a traditional feast characterized by elaborate toasts and a variety of dishes.
- National Holidays: Important holidays include Independence Day (May 26), St. George’s Day (November 23), and New Year’s Day.
Cuisine
Georgian cuisine is renowned for its diversity and flavor. Key dishes include:
- Khachapuri: A cheese-filled bread that is a staple in Georgian cuisine.
- Khinkali: Dumplings filled with meat, herbs, and spices.
- Pkhali: Vegetable dishes made with spinach, beets, or other greens, mixed with ground walnuts and spices.
- Wine: Georgia is one of the oldest wine-producing regions in the world, with a winemaking tradition dating back over 8,000 years.
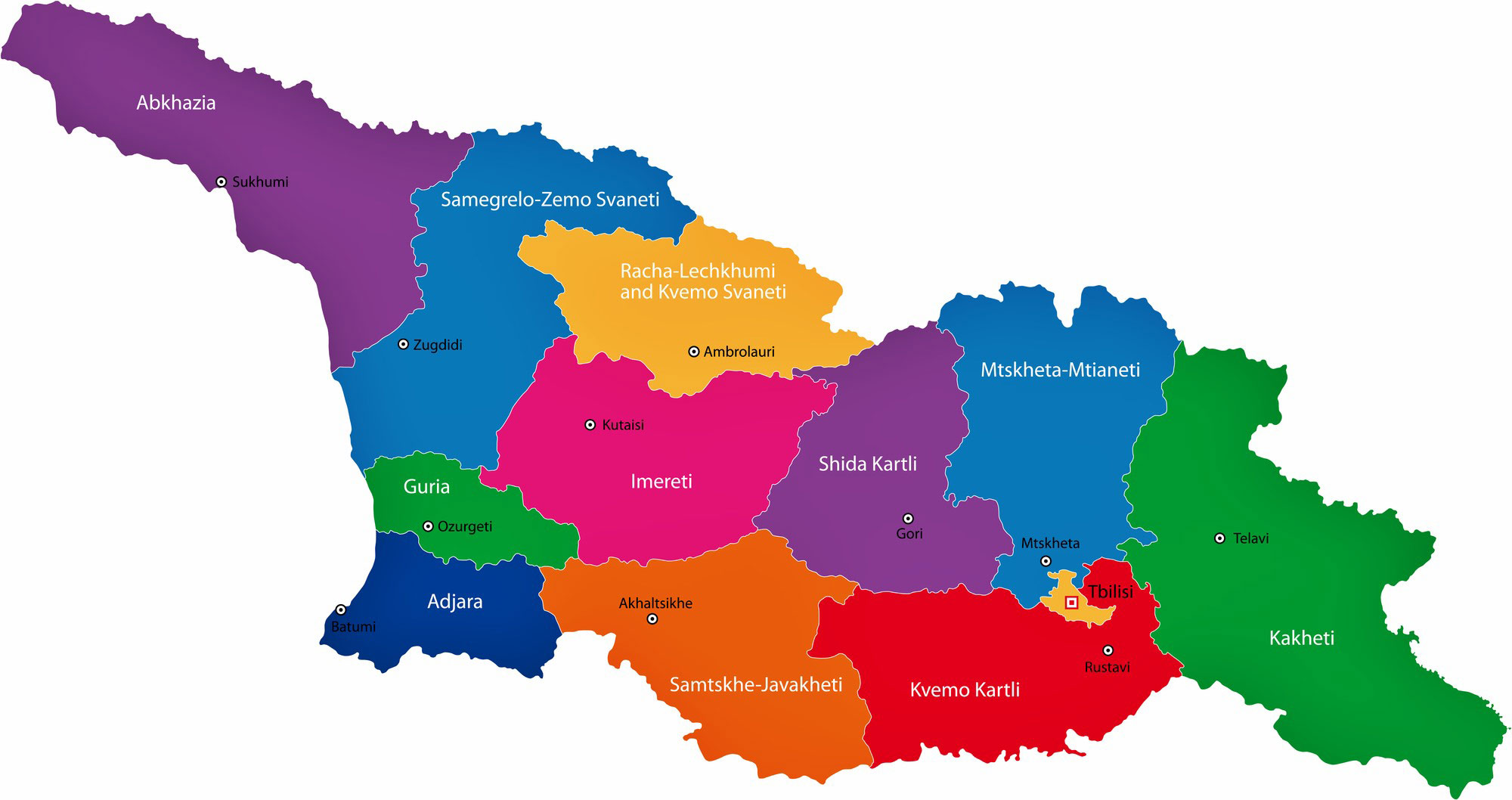
Maps of Georgia
Maps are essential for understanding the geography and regional distinctions within Georgia. Several types of maps provide different perspectives on the country.
Political Map
A political map of Georgia highlights its administrative divisions, including regions, municipalities, and major cities. Key cities include:
- Tbilisi: The capital and largest city, serving as the political, economic, and cultural center of the country.
- Kutaisi: The legislative capital and the seat of the Parliament of Georgia.
- Batumi: A major port city on the Black Sea and a popular tourist destination.
Physical Map
A physical map shows the natural features of Georgia, including mountains, rivers, and valleys. Key features include:
- Caucasus Mountains: Dominating the northern part of the country, with several peaks exceeding 5,000 meters.
- Rivers: The Mtkvari (Kura) River is the longest river in Georgia, flowing through Tbilisi and into the Caspian Sea.
- Lakes: Lake Paravani is the largest lake in Georgia.
Climate Map
A climate map of Georgia illustrates the diverse climatic zones across the country, from the humid subtropical climate of the western lowlands to the continental and alpine climates of the interior and mountainous regions.
Historical Map
Historical maps provide insight into the territorial changes and historical boundaries of Georgia over the centuries. These maps can show the extent of ancient kingdoms, the influence of various empires, and the modern borders established in the 20th century.
Interesting Facts About Georgia
- Oldest Wine Region: Archaeological evidence suggests that Georgia is the birthplace of winemaking, with a tradition dating back over 8,000 years.
- Alphabet: The Georgian alphabet is one of the 14 unique scripts in the world, with three writing systems used historically: Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri, and Mkhedruli.
- Hospitality: Georgian hospitality is legendary, with a saying that “a guest is a gift from God.” The supra (feast) is a central aspect of this tradition.
- UNESCO Sites: Georgia is home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the Historical Monuments of Mtskheta and the Gelati Monastery.
Commonly Asked Questions
How many regions are there in Georgia?
Georgia is divided into nine regions, one city (Tbilisi), and two autonomous republics (Abkhazia and Adjara).
What is the population of Georgia?
As of the latest estimates, the population of Georgia is approximately 3.7 million people.
What is the main economic activity in Georgia?
Key economic activities in Georgia include agriculture, tourism, mining, manufacturing, and services.
What languages are spoken in Georgia?
The official language is Georgian, but other languages such as Russian, Armenian, and Azerbaijani are also spoken by minority communities.
What are some famous tourist attractions in Georgia?
Notable tourist attractions include the ancient cave city of Uplistsikhe, the mountainous region of Svaneti, the coastal city of Batumi, and the capital city of Tbilisi with its historic old town.
Is Georgia part of the European Union?
No, Georgia is not a member of the European Union, but it has signed an Association Agreement with the EU and aspires to join in the future.
What is the significance of the Georgian Orthodox Church?
The Georgian Orthodox Church plays a central role in the country’s cultural and spiritual life, with a majority of Georgians identifying as Orthodox Christians.
How has Georgia’s economy evolved in recent years?
Georgia’s economy has seen significant growth and modernization since the early 2000s, with reforms aimed at improving the business environment and attracting foreign investment.
What is the role of wine in Georgian culture?
Wine is deeply embedded in Georgian culture and tradition, with a history of winemaking that dates back thousands of years. It is an integral part of the supra and social gatherings.
What are some key historical events in Georgia’s history?
Key historical events include the adoption of Christianity in the 4th century, the Golden Age under King David IV and Queen Tamar, annexation by the Russian Empire, Soviet rule, and independence in 1991.
Conclusion
Georgia is a country of remarkable diversity and rich cultural heritage, situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. From its stunning landscapes and ancient history to its vibrant culture and dynamic economy, Georgia offers a unique blend of old and new. This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth look at the country’s geography, history, political structure, economy, culture, and more, offering a thorough understanding of this fascinating nation.
- Hungary Maps & Facts - June 24, 2024
- The Bahamas Maps & Facts - June 13, 2024
- Colombia Maps & Facts - June 12, 2024