Introduction
Peru, a country in western South America, is known for its rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes. From the majestic peaks of the Andes to the lush Amazon rainforest, Peru offers a unique blend of natural beauty and historical intrigue. This guide will provide an in-depth look at Peru’s geography, history, culture, economy, and more, supported by maps and detailed facts.
Geography
Location and Borders
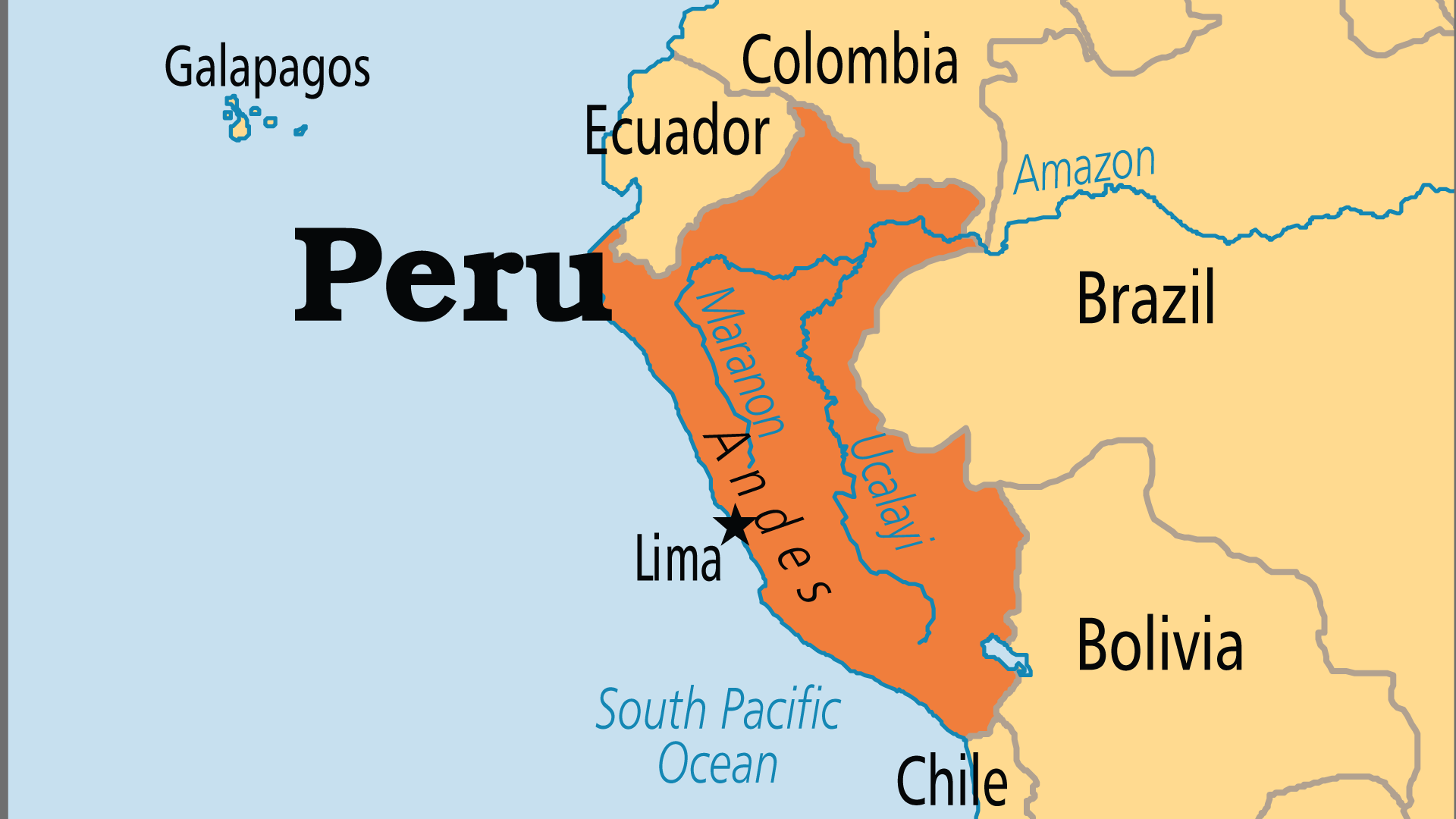
Peru is situated on the western edge of South America, bordered by Ecuador and Colombia to the north, Brazil to the east, Bolivia to the southeast, Chile to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It lies between latitudes 0° and 18°S and longitudes 68° and 81°W.
Topography
Peru’s topography is incredibly varied, comprising three distinct geographical regions
The Coastal Region (La Costa)
A narrow strip along the Pacific Ocean, characterized by deserts and fertile valleys. Major cities like Lima, the capital, and Trujillo are located here.
The Highland Region (La Sierra)
Dominated by the Andes Mountains, this region includes Peru’s highest peak, Huascarán, standing at 6,768 meters (22,205 feet). The highlands are home to famous sites such as Machu Picchu and Cusco, the former capital of the Inca Empire.
The Jungle Region (La Selva)
The vast Amazon Basin covers about 60% of Peru, making it a significant portion of the country’s land area. This region is rich in biodiversity and includes the Manu and Tambopata National Parks.
Climate
Peru’s climate varies significantly due to its diverse topography:
- Coastal Region: Arid and semi-arid with little rainfall. Lima, for instance, has a mild climate with high humidity.
- Highland Region: Experiences a cooler climate with significant temperature variations between day and night. Rainy season typically runs from December to March.
- Jungle Region: Hot and humid year-round with heavy rainfall, particularly from November to March.
History
Pre-Columbian Civilizations
Peru is the cradle of several advanced pre-Columbian civilizations:
- Norte Chico Civilization: One of the oldest in the Americas, flourishing around 3000-1800 BCE.
- Moche and Nazca: Known for their impressive ceramics, textiles, and geoglyphs.
- Inca Empire: The largest empire in pre-Columbian America, with its capital at Cusco. The Inca were renowned for their sophisticated agricultural techniques, architecture, and road systems.
Spanish Conquest
In 1532, Spanish conquistador Francisco Pizarro captured the Inca emperor Atahualpa, leading to the fall of the Inca Empire. Spain subsequently established the Viceroyalty of Peru, which became a major colonial center until Peru declared its independence on July 28, 1821.
Modern History
Post-independence, Peru has experienced periods of political instability, economic challenges, and social unrest. Significant events include:
- War of the Pacific (1879-1884): Conflict with Chile, resulting in Peru losing territory.
- Shining Path Insurgency (1980s-1990s): A violent conflict involving the Maoist guerrilla group Shining Path, leading to widespread violence and human rights abuses.
Today, Peru is a democratic republic with a growing economy, although challenges such as poverty and corruption persist.
Culture
Language
Spanish is the official language of Peru, spoken by approximately 84% of the population. Quechua, the language of the Inca Empire, and Aymara are also recognized as official languages and are spoken in various regions, particularly in the highlands.
Religion
Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion, practiced by around 76% of Peruvians. The country also has vibrant Protestant, Evangelical, and indigenous spiritual communities.
Festivals
Peru is known for its colorful and vibrant festivals, often blending indigenous traditions with Catholic influences:
- Inti Raymi: The Inca Festival of the Sun, celebrated in Cusco every June 24.
- Fiesta de la Candelaria: Held in Puno, this festival honors the Virgin of Candelaria with traditional dances and music.
- Carnaval: Celebrated nationwide with parades, music, and water fights.
Cuisine
Peruvian cuisine is diverse and flavorful, reflecting its varied geography and cultural influences:
- Ceviche: A dish made from fresh raw fish marinated in citrus juices, typically served with onions, chili peppers, and cilantro.
- Lomo Saltado: A stir-fry dish combining marinated strips of beef with onions, tomatoes, and fries, often served with rice.
- Ají de Gallina: Shredded chicken in a creamy, spicy sauce made with ají peppers and walnuts.
Economy
Overview
Peru’s economy is classified as upper-middle income by the World Bank. It is one of the fastest-growing economies in Latin America, driven by sectors such as mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism.
Key Industries
- Mining: Peru is a leading producer of gold, silver, copper, zinc, and lead. The mining industry is a significant contributor to the country’s GDP and export revenues.
- Agriculture: Major agricultural exports include coffee, asparagus, and avocados. The country is also known for its production of traditional crops like potatoes and quinoa.
- Tourism: Attracts millions of visitors annually, drawn by the country’s historical sites, natural beauty, and cultural festivals.
Trade
Peru has numerous trade agreements with countries and economic blocs, including the United States, the European Union, China, and other Latin American nations. These agreements facilitate the export of goods and services, bolstering economic growth.
Maps of Peru
Political Map
A political map of Peru shows the country’s administrative divisions, including its 25 regions (departments) and their capitals. Key cities such as Lima (the capital), Arequipa, Trujillo, and Cusco are highlighted.
Physical Map
A physical map of Peru highlights its diverse geography, including:
- The Andes Mountains running along the western edge.
- The vast Amazon Basin covering the eastern part.
- Coastal deserts and fertile valleys in the west.
Tourist Map
A tourist map of Peru showcases major attractions and landmarks, such as:
- Machu Picchu
- The Sacred Valley
- Lake Titicaca
- The Nazca Lines
- Colca Canyon
Fun Fact About Peruvian Maps
Did you know? The ancient Inca civilization was known for its advanced system of roads and bridges, which spanned over 40,000 kilometers (25,000 miles). This network, known as the Qhapaq Ñan, connected various parts of the empire and is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Peru
What is the capital of Peru?
The capital of Peru is Lima, a bustling metropolis located on the country’s central coast.
What is Peru famous for?
Peru is famous for its rich history, particularly the Inca civilization and the iconic archaeological site of Machu Picchu. The country is also known for its diverse landscapes, including the Andes Mountains, the Amazon rainforest, and beautiful coastal regions.
What languages are spoken in Peru?
The official languages of Peru are Spanish, Quechua, and Aymara. Spanish is the most widely spoken language, while Quechua and Aymara are prevalent in specific regions, particularly in the highlands.
What are some traditional Peruvian dishes?
Some traditional Peruvian dishes include ceviche, lomo saltado, ají de gallina, causa, and anticuchos. These dishes reflect the country’s diverse culinary heritage and use a variety of local ingredients.
What is the climate like in Peru?
Peru’s climate varies by region. The coastal region is arid and mild, the highlands experience a cooler and variable climate, and the jungle region is hot and humid with heavy rainfall.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Peru?
Popular tourist attractions in Peru include Machu Picchu, the Sacred Valley, Cusco, Lake Titicaca, the Nazca Lines, and the Amazon rainforest.
How important is mining to Peru’s economy?
Mining is a crucial sector in Peru’s economy, contributing significantly to GDP and export revenues. Peru is a leading producer of minerals such as gold, silver, copper, zinc, and lead.
What are Peru’s major agricultural exports?
Peru’s major agricultural exports include coffee, asparagus, avocados, grapes, and blueberries. The country is also known for producing traditional crops like potatoes and quinoa.
How does Peru’s geography influence its culture?
Peru’s diverse geography, which includes coastal deserts, highland mountains, and tropical rainforests, has significantly influenced its culture. This diversity is reflected in regional customs, traditional clothing, and culinary practices.
What is the significance of the Qhapaq Ñan?
The Qhapaq Ñan, also known as the Inca Road System, is a vast network of roads and bridges built by the Inca civilization. It connected various parts of the empire and facilitated trade, communication, and military movements. Today, it is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Conclusion
Peru is a country of remarkable contrasts, offering a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. Its diverse geography ranges from coastal deserts to towering mountains and lush rainforests, each contributing to the nation’s unique identity. From the ancient mysteries of the Inca Empire to the vibrant modern culture, Peru continues to captivate and inspire those who explore its many facets. Whether you’re drawn to its historical sites, culinary delights, or stunning landscapes, Peru is a destination that promises a wealth of experiences and insights.
- Ecuador Maps & Facts - July 12, 2024
- Is England Part of Europe? - July 2, 2024
- Guatemala Maps & Facts - June 29, 2024