Introduction to Mauritius
Mauritius, an island nation located in the Indian Ocean, is renowned for its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and diverse ecosystems. This guide provides an in-depth look into the geography, history, culture, economy, and demographics of Mauritius, offering a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating country.
Geography of Mauritius
Location and Size
Mauritius is situated in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometers off the southeastern coast of Africa, east of Madagascar. The island covers an area of approximately 2,040 square kilometers, making it relatively small but densely populated. The country comprises the main island of Mauritius and several smaller islands and islets, including Rodrigues, Agalega, and the Cargados Carajos Shoals (Saint Brandon).
Topography and Landscape
The island’s topography is characterized by a central plateau surrounded by mountains. The highest peak, Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire, reaches 828 meters. The landscape features lush green forests, rolling hills, and stunning coastlines with white sandy beaches and coral reefs. The interior is dotted with sugarcane fields, reflecting the island’s agricultural heritage.
Climate
Mauritius enjoys a tropical climate, with warm and humid weather throughout the year. The island has two main seasons: a warm, wet summer from November to April and a cooler, dry winter from May to October. Cyclones can occur during the summer months, bringing heavy rains and strong winds.
Historical Background of Mauritius
Early History and Colonization
The island of Mauritius was uninhabited until it was discovered by Arab sailors in the 10th century. The Portuguese were the first Europeans to visit the island in the early 16th century. However, it was the Dutch who first settled the island in 1638, naming it Mauritius after Prince Maurice of Nassau. The Dutch abandoned the island in 1710 due to difficult living conditions.
French and British Rule
The French took control of Mauritius in 1715, renaming it Île de France. They established a prosperous colony based on sugarcane plantations and introduced African slaves to work on the fields. In 1810, during the Napoleonic Wars, the British captured the island and reverted its name to Mauritius. Under British rule, the island saw significant economic development and the abolition of slavery in 1835.
Independence and Modern Era
Mauritius gained independence from the United Kingdom on March 12, 1968. Since then, it has evolved into a stable and prosperous nation with a diverse economy. The country is known for its political stability, strong institutions, and vibrant democracy.
Culture and Society of Mauritius
Ethnic Diversity
Mauritius is a melting pot of cultures, with a population that includes people of Indian, African, Chinese, and European descent. This diversity is reflected in the island’s rich cultural heritage, traditions, and festivals. Hinduism, Christianity, and Islam are the major religions practiced in Mauritius, contributing to its multicultural society.
Languages
The official language of Mauritius is English, but French and Mauritian Creole are widely spoken. Mauritian Creole, derived from French, is the lingua franca and is spoken by the majority of the population. Several other languages, including Hindi, Urdu, and Chinese, are also spoken among various ethnic communities.
Festivals and Traditions
Mauritius celebrates a variety of religious and cultural festivals throughout the year. Notable festivals include Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights; Eid al-Fitr, marking the end of Ramadan for Muslims; and Chinese New Year. The island also celebrates its independence day on March 12 with parades and cultural events.
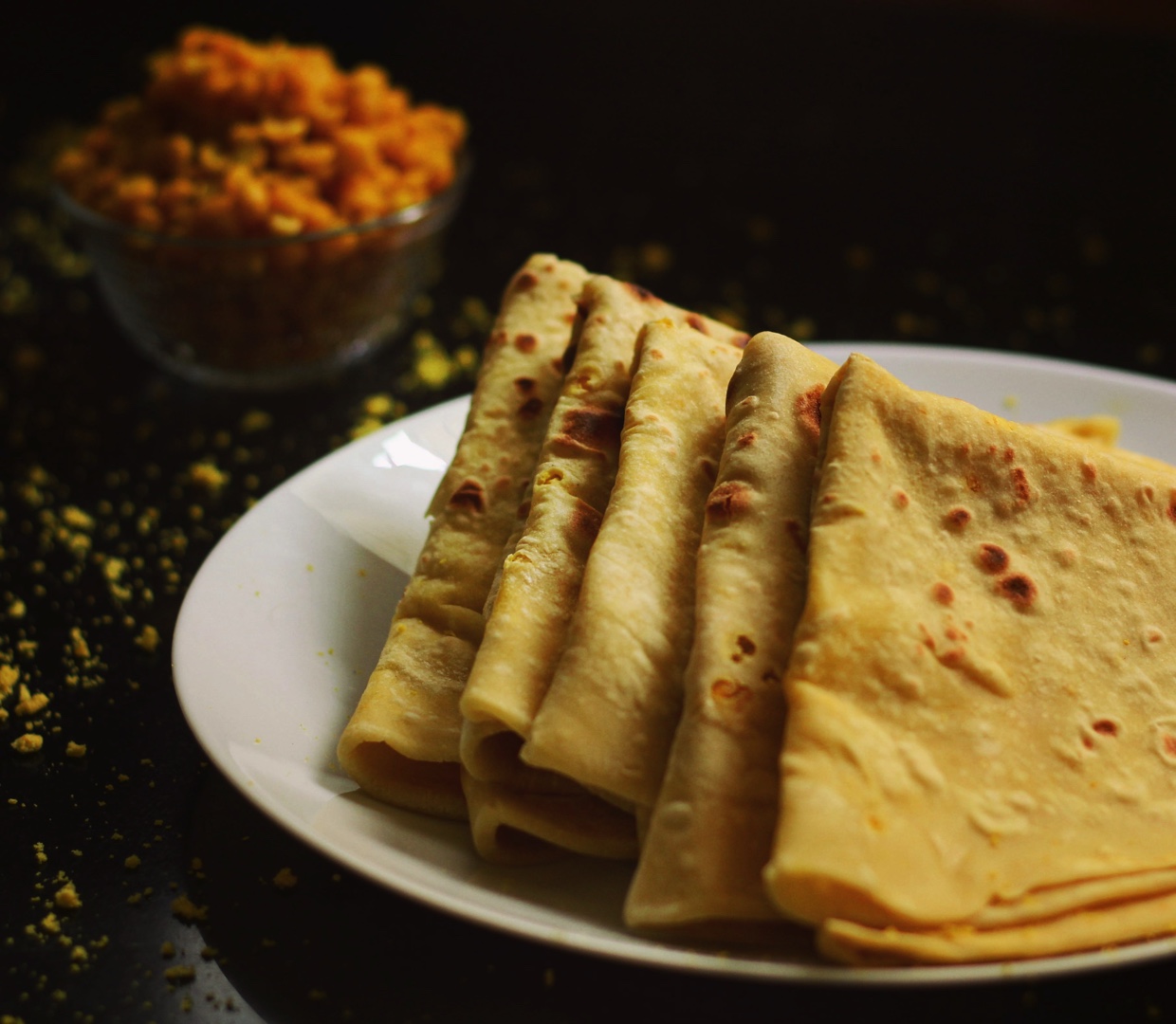

Cuisine
Mauritian cuisine is a reflection of its diverse population. It combines elements of Indian, African, Chinese, and European cooking. Popular dishes include dholl puri (a type of flatbread), biryani, rougaille (a tomato-based dish), and gateau piment (chili cakes). Seafood is also a staple, given the island’s proximity to the ocean.
Economy of Mauritius
Economic Overview
Mauritius has transformed from a low-income, agriculture-based economy to an upper-middle-income diversified economy. Key sectors include tourism, textiles, sugar, and financial services. The country is also developing its information and communication technology (ICT) sector and is a hub for offshore business activities.
Tourism
Tourism is a significant contributor to the Mauritian economy. The island’s pristine beaches, luxury resorts, and unique natural attractions draw visitors from around the world. Key tourist spots include the Black River Gorges National Park, Chamarel Seven Coloured Earths, and Île aux Cerfs.
Agriculture
Sugarcane has historically been the backbone of the Mauritian economy. Although its importance has declined, it remains a vital agricultural product. The island also produces tea, tropical fruits, and vegetables. Efforts are being made to diversify agriculture and promote sustainable farming practices.
Industry and Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector in Mauritius includes textiles, apparel, and electronics. The country is known for its high-quality textiles and garments, which are exported globally. The government encourages foreign investment and provides incentives for businesses to set up manufacturing operations on the island.
Demographics of Mauritius
Population Overview
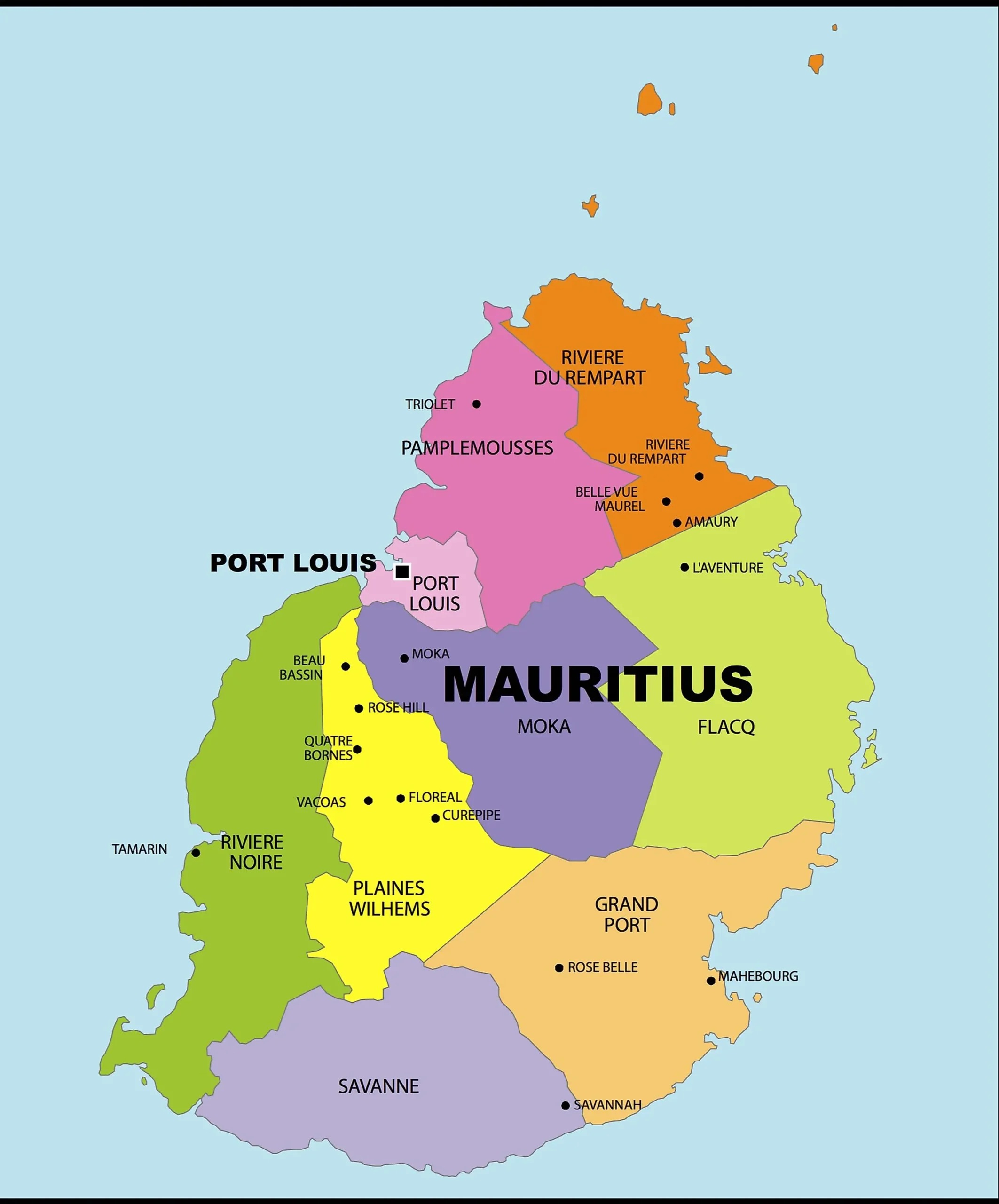
As of 2023, the population of Mauritius is estimated to be around 1.3 million people. The island has a high population density, particularly in urban areas. The capital city, Port Louis, is the most populous city, followed by cities like Beau Bassin-Rose Hill, Vacoas-Phoenix, and Curepipe.
Urbanization
Mauritius is highly urbanized, with over 40% of the population living in urban areas. Port Louis, the capital and largest city, is the economic and cultural hub of the island. The city is known for its bustling markets, colonial architecture, and vibrant waterfront.
Education and Health
Mauritius boasts a high literacy rate, with free education provided from primary to tertiary levels. The island has several universities and technical institutions. The healthcare system is well-developed, with both public and private healthcare services available to the population.
Fun and Interesting Facts About Mauritius
Unique Biodiversity
Mauritius is home to a rich variety of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to the island. The dodo, an extinct flightless bird, was native to Mauritius and has become a symbol of the island’s unique biodiversity. The Black River Gorges National Park is a key conservation area, protecting the island’s remaining indigenous forests and wildlife.
Famous Mauritians
Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam, known as the “Father of the Nation,” was the first Prime Minister of independent Mauritius. His contributions to the country’s independence and development are celebrated annually on March 18, his birthday. Another notable Mauritian is Jean-Marie Gustave Le Clézio, a Nobel Prize-winning author.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
Mauritius is home to two UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Aapravasi Ghat and Le Morne Cultural Landscape. Aapravasi Ghat is the site where indentured laborers from India first arrived in Mauritius. Le Morne Cultural Landscape is a mountain that served as a refuge for runaway slaves, symbolizing the island’s history of resistance and freedom.
Commonly Asked Questions About Mauritius
What is the capital of Mauritius?
The capital of Mauritius is Port Louis, located on the northwest coast of the island. It is the country’s largest city and serves as the political, economic, and cultural center.
What currency is used in Mauritius?
The currency used in Mauritius is the Mauritian rupee (MUR).
Is Mauritius a safe country to visit?
Mauritius is generally considered a safe country for tourists. However, like any destination, it is advisable to take standard safety precautions, such as avoiding isolated areas at night and safeguarding personal belongings.
What are the official languages of Mauritius?
The official language of Mauritius is English. However, French and Mauritian Creole are widely spoken, with Creole being the most commonly used language in everyday conversation.
What are the major industries in Mauritius?
The major industries in Mauritius include tourism, textiles, sugar, and financial services. The country is also developing its ICT sector and attracting offshore business activities.
What is the climate like in Mauritius?
Mauritius has a tropical climate with warm and humid weather year-round. The island experiences a warm, wet summer from November to April and a cooler, dry winter from May to October.
What is the population of Mauritius?
As of 2023, the population of Mauritius is estimated to be around 1.3 million people.
Are there any unique wildlife species in Mauritius?
Yes, Mauritius is home to several unique wildlife species, many of which are endemic to the island. The dodo, an extinct flightless bird, was native to Mauritius. The island also has rare plants and animals protected in conservation areas like the Black River Gorges National Park.
What are the main attractions for tourists in Mauritius?
Main attractions in Mauritius include its pristine beaches, Black River Gorges National Park, Chamarel Seven Coloured Earths, Île aux Cerfs, and historical sites like Aapravasi Ghat and Le Morne Cultural Landscape.
What is the significance of the dodo in Mauritius?
The dodo is significant to Mauritius as an emblem of its unique biodiversity and a stark reminder of human impact on the environment, symbolizing both the island’s ecological richness and the consequences of extinction.
- 10 Most Beautiful Ozark Mountain Towns - September 3, 2024
- Countries That Start With The Letter Q - September 3, 2024
- 10 Largest Cities In Nebraska - September 2, 2024