Palestine, a region with a profound historical and cultural significance, is situated in the Middle East and has been a focal point of geopolitical interest and conflict for centuries. This comprehensive guide explores the geography, history, culture, and contemporary issues surrounding Palestine, supplemented with detailed maps and facts to provide a holistic understanding of this unique region.
Introduction to Palestine
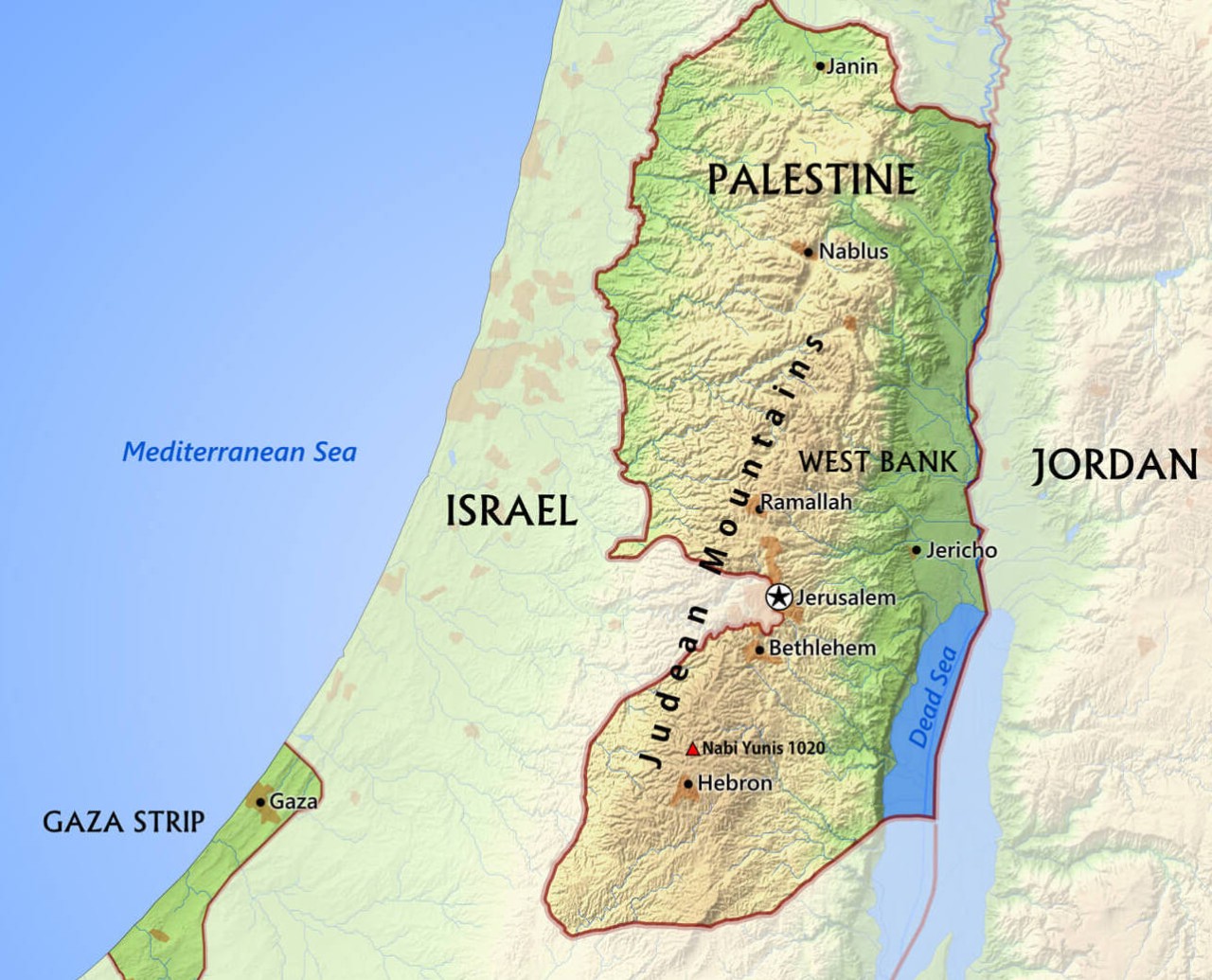
Palestine is a geographical and historical region in the Middle East, comprising parts of modern-day Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip. It is a land rich in cultural heritage and historical significance, known as the birthplace of major world religions such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The region has been a center of conflict and political tension, particularly between Israelis and Palestinians, making its study essential for understanding contemporary Middle Eastern geopolitics.
Geographic Overview
Location and Boundaries
Palestine is located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest, and Israel to the west and northwest. The West Bank and Gaza Strip are the primary territories under Palestinian administration.
Topography and Climate
The region’s topography is diverse, featuring coastal plains, central highlands, and the Jordan Rift Valley. The climate varies from Mediterranean along the coast, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, to semi-arid and arid conditions in the interior and southern parts.
Key Geographic Features
- Jordan River: A significant waterway that flows from the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea, playing a crucial role in the region’s agriculture and history.
- Dead Sea: The lowest point on Earth’s surface, renowned for its high salinity and mineral-rich waters.
- Mount of Olives: An important religious site in East Jerusalem with historical and biblical significance.
Historical Context
Ancient History
Palestine’s history dates back to ancient times, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Paleolithic era. It has been home to various civilizations, including the Canaanites, Egyptians, Israelites, Philistines, Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Greeks, and Romans.
Biblical Significance
Palestine is often referred to as the Holy Land, with numerous sites of religious importance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Jerusalem, Hebron, Bethlehem, and Nazareth are cities with profound biblical associations.
Islamic Conquests and Ottoman Rule
After the Islamic conquests in the 7th century, Palestine became part of the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates. It was later controlled by the Ottoman Empire from the 16th century until the early 20th century.
20th Century and Modern History
British Mandate and the Creation of Israel
Following World War I, the League of Nations granted Britain the mandate to govern Palestine. The Balfour Declaration of 1917 expressed British support for a “national home for the Jewish people” in Palestine, leading to increased Jewish immigration. In 1948, the State of Israel was declared, leading to the first Arab-Israeli war and significant displacement of Palestinians.
Palestinian Territories and Governance
The 1967 Six-Day War resulted in Israel occupying the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Subsequent peace efforts, such as the Oslo Accords, established the Palestinian Authority (PA) to administer parts of these territories, though full sovereignty remains a contentious issue.
Cultural and Demographic Aspects
Population and Ethnic Groups
Palestine’s population is predominantly Arab, with Palestinian Muslims forming the majority. There are also Christian and smaller Samaritan communities. The Palestinian diaspora is significant, with millions of Palestinians living in refugee camps or settled in other countries, primarily in the Middle East.
Languages and Religion
Arabic is the official and most widely spoken language. English is also commonly used, especially in business and government. Islam is the dominant religion, followed by Christianity, with both faiths playing a vital role in the cultural identity of Palestinians.
Traditions and Cultural Heritage
Cuisine
Palestinian cuisine is a blend of Mediterranean and Middle Eastern flavors, featuring dishes like hummus, falafel, tabbouleh, and maqluba. Olive oil, herbs, and spices are staples in Palestinian cooking.
Music and Dance
Traditional Palestinian music often includes instruments like the oud, qanun, and darbuka. The dabke, a traditional folk dance, is performed at weddings and celebrations, symbolizing communal solidarity and joy.
Arts and Crafts
Palestinian embroidery, known as “tatreez,” is a distinctive and culturally significant craft, often featuring geometric and floral patterns. Pottery, glassblowing, and olive wood carvings are also important cultural expressions.
Political Landscape
Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a longstanding and complex dispute over land, identity, and sovereignty. Key issues include the status of Jerusalem, borders, security, the right of return for Palestinian refugees, and mutual recognition.
Peace Efforts and Agreements
Various peace efforts have been made, including the Camp David Accords, Oslo Accords, and more recent initiatives like the Trump administration’s “Peace to Prosperity” plan. However, a lasting resolution remains elusive.
Governance and Administration
The Palestinian Authority governs parts of the West Bank, while the Gaza Strip is controlled by Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist political organization. The division of governance between the West Bank and Gaza presents additional challenges for Palestinian unity and political stability.
Economy and Infrastructure
Economic Overview
Palestine’s economy is mixed, with agriculture, industry, and services sectors. Key agricultural products include olives, citrus fruits, vegetables, and livestock. The industrial sector encompasses textiles, food processing, and handicrafts.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Palestinian economy faces significant challenges, including restrictions on movement and access, limited natural resources, political instability, and reliance on donor aid. However, there are opportunities for growth in technology, tourism, and renewable energy.
Infrastructure and Development
Infrastructure development in Palestine is constrained by political and logistical challenges. However, efforts are being made to improve transportation, healthcare, education, and housing to enhance the quality of life for Palestinians.
Maps of Palestine
Historical Maps
Historical maps of Palestine provide valuable insights into the region’s changing boundaries and political landscape over centuries. They highlight the territorial shifts from ancient civilizations through Ottoman rule to the modern era.
Contemporary Maps
Modern maps of Palestine depict the current political and administrative divisions, including the West Bank and Gaza Strip, Israeli settlements, and areas under Palestinian Authority control. These maps are essential for understanding the geographical and political complexities of the region.
Thematic Maps
Thematic maps focus on specific aspects such as population density, religious sites, natural resources, and economic activities. These maps offer a deeper understanding of the various factors influencing life in Palestine.
Key Facts About Palestine
- Capital: East Jerusalem (claimed), Ramallah (administrative)
- Population: Approximately 5 million (West Bank and Gaza Strip)
- Official Language: Arabic
- Major Religions: Islam, Christianity
- Currency: Israeli Shekel (ILS), Jordanian Dinar (JOD), Egyptian Pound (EGP)
- Time Zone: Eastern European Time (EET), UTC +2
Fun and Interesting Facts
Cultural Heritage
Palestine is home to some of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, including Jericho, which dates back over 10,000 years.
Religious Significance
The Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem, believed to be the birthplace of Jesus Christ, is one of the oldest surviving Christian churches and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Natural Wonders
The Dead Sea, located along the border of Palestine and Jordan, is the lowest point on Earth’s surface and is renowned for its therapeutic properties due to its high mineral content.
Literary and Artistic Contributions
Palestinian poet Mahmoud Darwish is celebrated internationally for his powerful and evocative poetry, which reflects the Palestinian experience and struggle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the West Bank and Gaza Strip?
The West Bank and Gaza Strip are key territories in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with both areas under Palestinian administration but facing significant Israeli control and restrictions. They are central to discussions on Palestinian statehood and sovereignty.
What are some major cities in Palestine?
Major cities in Palestine include Jerusalem (East Jerusalem), Ramallah, Bethlehem, Hebron, Nablus, and Gaza City. Each city has its own historical, cultural, and political significance.
How does the international community view Palestine?
The international community is divided in its recognition of Palestine. Some countries and organizations recognize it as a sovereign state, while others, including Israel and some Western countries, do not. The United Nations grants Palestine non-member observer state status.
What are the main economic activities in Palestine?
The main economic activities in Palestine include agriculture (olives, citrus fruits, vegetables), industry (textiles, food processing), and services. Tourism also plays a significant role, especially in cities with religious and historical sites.
How does the education system work in Palestine?
The education system in Palestine is divided into three levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Education is highly valued, with a high literacy rate among the population. Universities and colleges in the West Bank and Gaza Strip offer a range of academic programs.
What is the cultural significance of Palestinian embroidery?
Palestinian embroidery, or “tatreez,” is a traditional art form that reflects the region’s cultural heritage. It often features geometric and floral patterns, with each design having specific meanings and associations with different regions and communities.
What are some popular Palestinian dishes?
Popular Palestinian dishes include hummus, falafel, maqluba (a layered rice and meat dish), musakhan (roasted chicken with onions and sumac), and knafeh (a sweet cheese pastry). These dishes highlight the rich culinary traditions of the region.
How has the Israeli-Palestinian conflict affected daily life in Palestine?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has profoundly impacted daily life in Palestine, leading to restrictions on movement, economic hardships, and social tensions. Despite these challenges, Palestinians continue to maintain their cultural identity and resilience.
What efforts are being made to promote peace in the region?
Various efforts to promote peace include diplomatic negotiations, international mediation, grassroots initiatives, and cultural exchanges. Organizations and individuals on both sides continue to work towards a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
What role does religion play in Palestinian society?
Religion plays a central role in Palestinian society, with Islam being the predominant faith, followed by Christianity. Religious practices and traditions are integral to daily life, influencing social norms, festivals, and cultural expressions.
Conclusion
Palestine is a region of immense historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance. Its complex history, rich cultural heritage, and ongoing challenges make it a fascinating and essential area of study. By understanding the maps and facts of Palestine, we gain deeper insights into its past, present, and potential future, fostering a more comprehensive appreciation of this unique and resilient region.
- 10 Biggest Urban Parks In The World - September 30, 2024
- 10 Animals Found In Brazil - September 29, 2024
- The Best Small Towns To Retire In Virginia - September 21, 2024